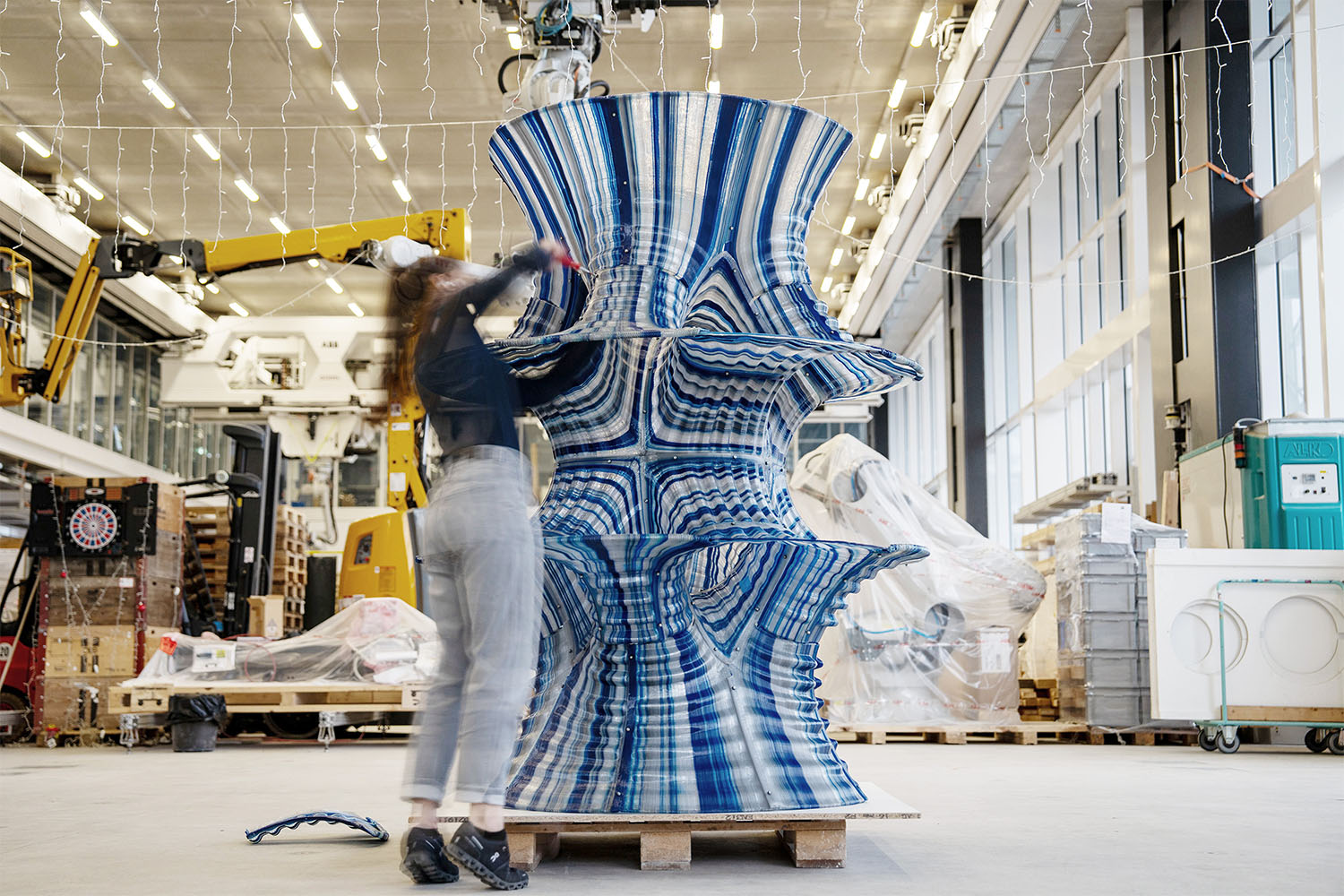
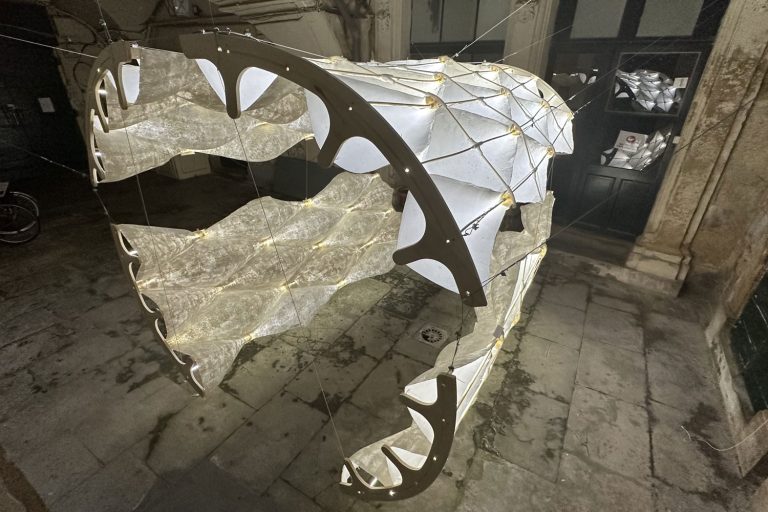
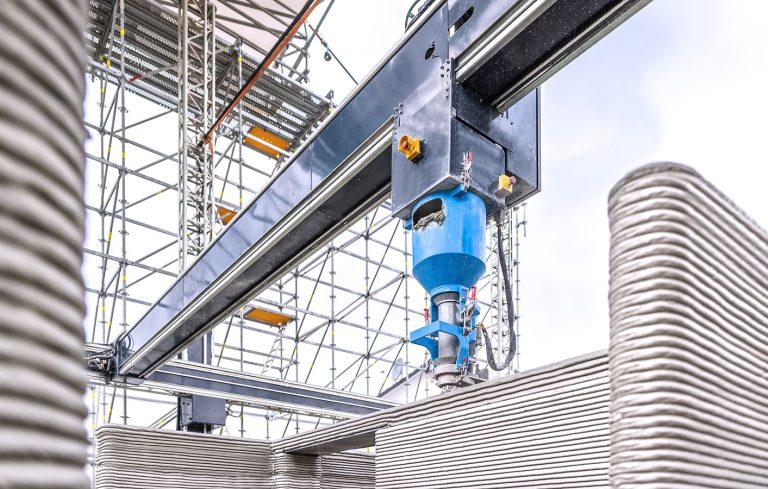
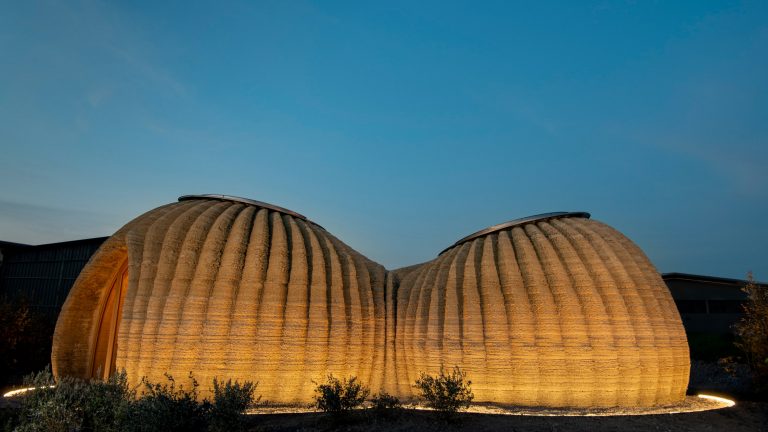
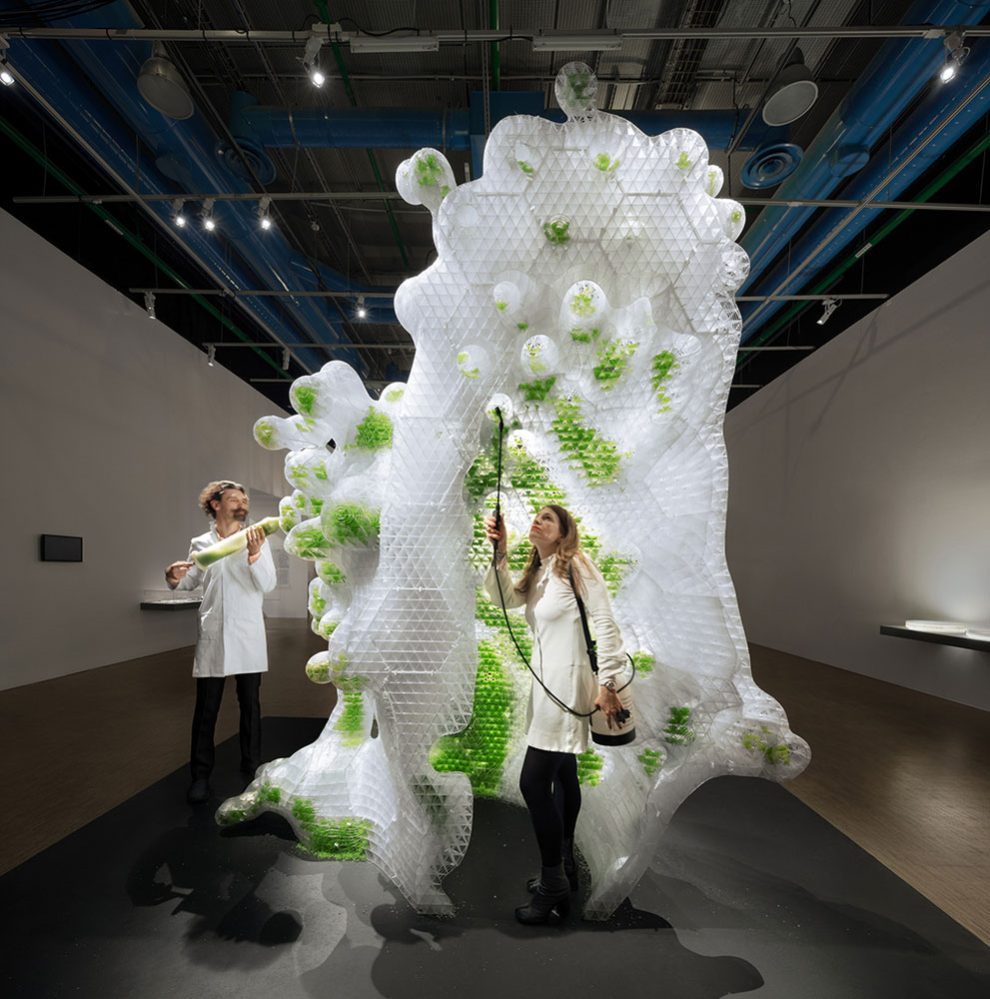
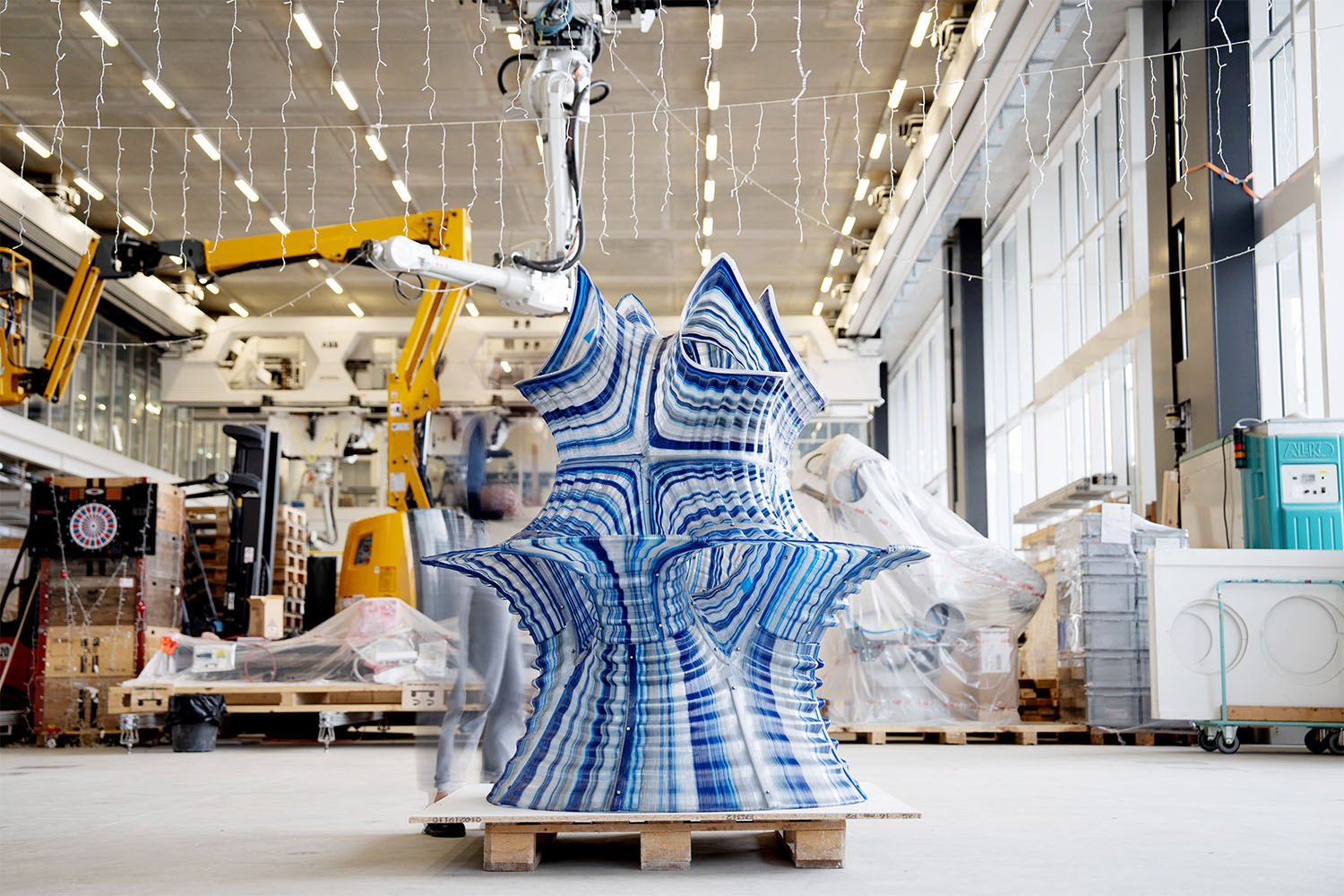
Fluid Forms is a 2.0-meter tall lightweight shell created using non-planar robotic 3D printing. This project showcases an innovative robotic additive manufacturing method that enables the more efficient printing of doubly curved thin shells.
“In this work, we present a methodology for generating and editing transversal strip networks aligned with user-defined directions, while also enabling the incorporation of desirable properties for the fabrication of the strips. The type of geometries we address is relatively smooth geometries with open boundaries and without significant surface detail features.” states the research paper.
The design is inspired by the Costa minimal surface, which is a shape that minimizes the area for a given boundary, resulting in a geometry with unique structural properties. The print paths are aligned to their principal curvature directions, which reduces the need for support and enhances precision and surface quality in high-curvature areas.
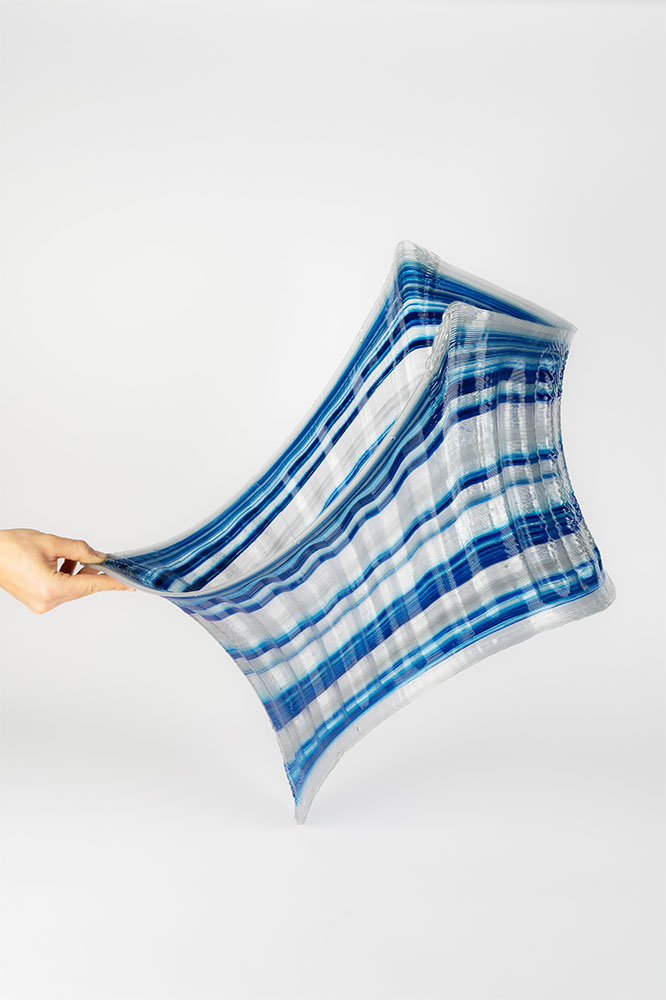
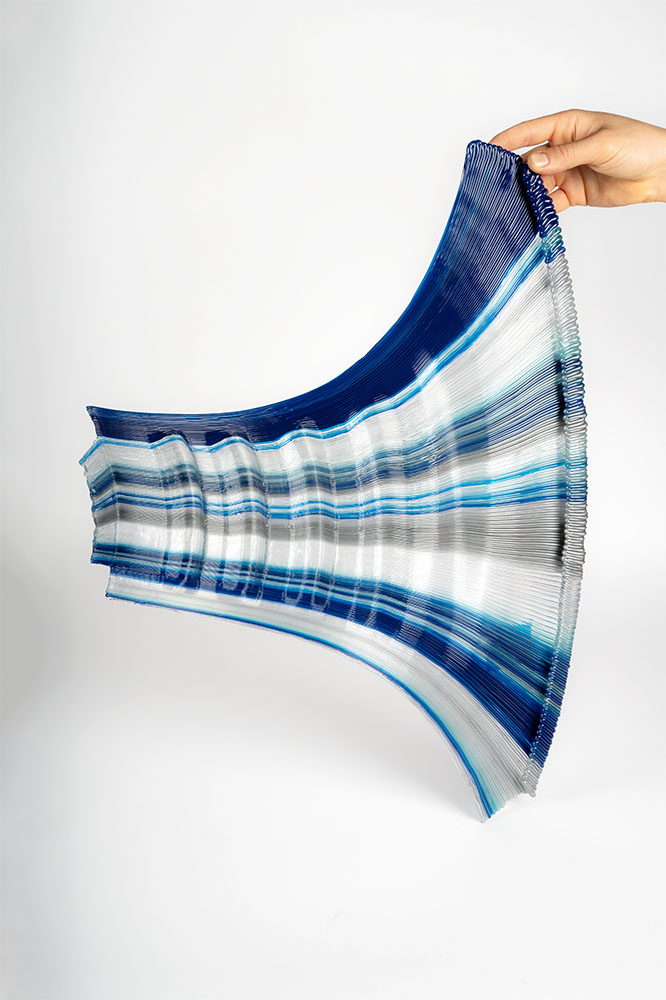
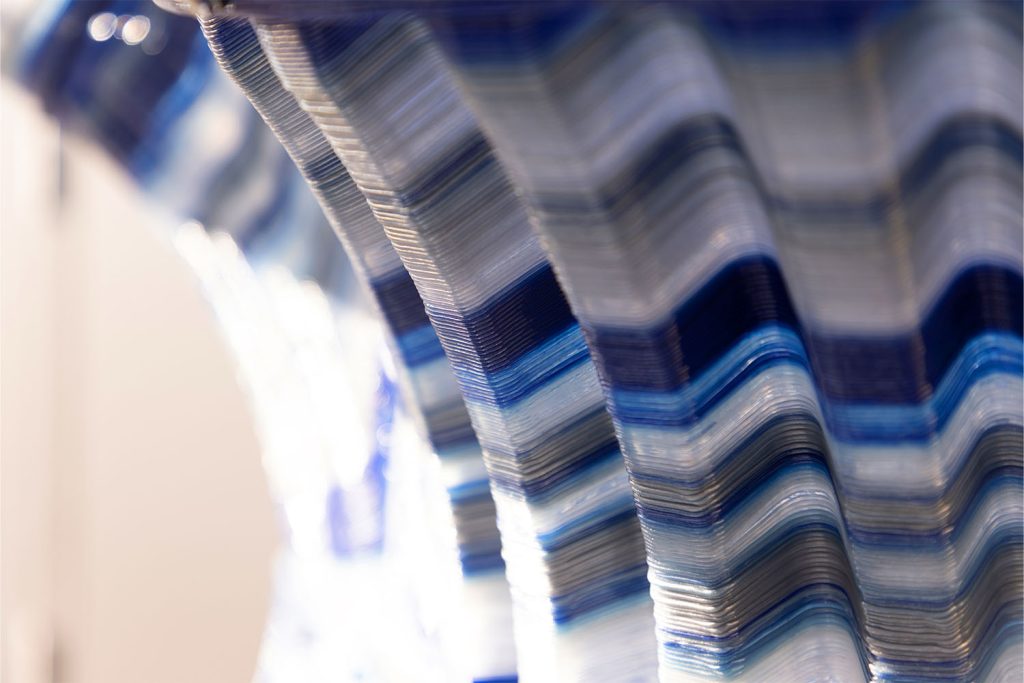



The print path orientation is controlled through a vector-field optimization method that has been fine-tuned for the specific needs and constraints of non-planar 3D printing. To increase the rigidity of the structure, undulations are introduced that are orthogonal to the print direction. The shell is made up of 40 parts held together using screws and assembled using a dry-assembly method that facilitates easy disassembly for recycling after the project’s lifetime.
Fluid Forms weighs 120 kilograms and has dimensions of 200cm in height and 140cm in width. The material used is translucent PETG plastic intermixed with blue and silver colors at varying ratios. The 3D printing process duration was approximately 3 weeks, a total of 140 hours of machining time.

Project Info
Digital Building Technologies, ETH Zurich
Design and Fabrication: Ioanna Mitropoulou
Advisors: Prof. Benjamin Dillenburger, Prof. Olga Diamanti, Prof. Amir Vaxman.
Technical support: Tobias Hartmann, Philippe Fleischmann, Matthias Leschok.
Documentation: Dominik Vogel, Andrei Jipa
Photography: Andrei Jipa, Dominik Vogel, Ioanna Mitropoulou