What is 3D-Printing?
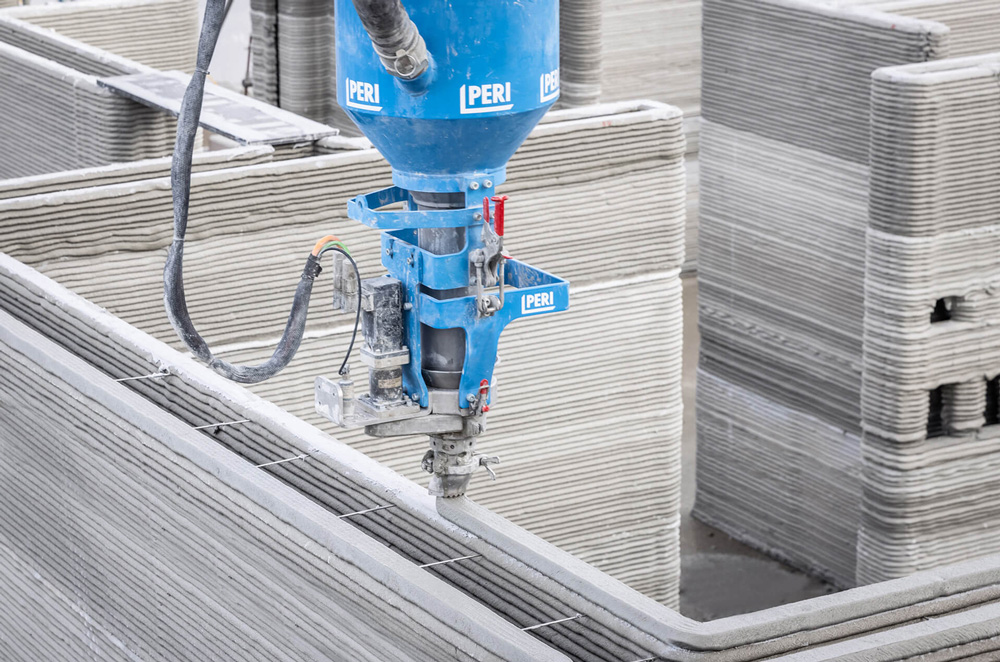
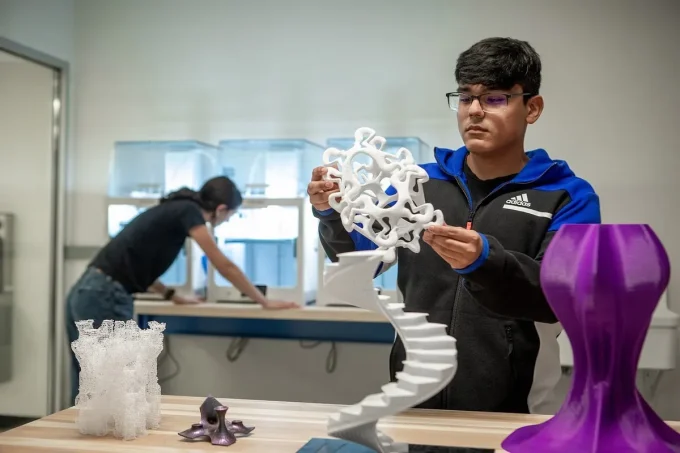
3D printing is the process of creating physical items by layering materials based on the requirements of a digital model. When compared to other conventional manufacturing processes, 3D Printing is highly advantageous since it can create new products very quickly and precisely. 3D printing is an established technology that has a much easier procedure than you would ever imagine.
Learn parametric design and computational tools from the pioneers of the industry at the PAACADEMY:
A History of 3D Printing
The earliest evidence of 3D printing can be found in Japan in the 1980s when Hideo Kodama was attempting to design a quick prototyping method. He devised a layer-by-layer manufacturing method that used a photosensitive resin polymerized by UV radiation. Later, Charles Hull developed the first SLA 3D printer in 1988. He devised a technology for manufacturing 3D models by curing photosensitive resins with radiation, particles, or lasers. Additionally, Carl Deckard patented the SLS process for 3D printing. Finally, Scott Crump invented Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) during the same period.
Although these were the foundations of 3D printing manufacturing processes, additional 3D printing techniques such as Digital Light Process (DLP), Multi Jet Fusion (MJF), PolyJet, Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), and Electron Beam Melting (EBM) exist.
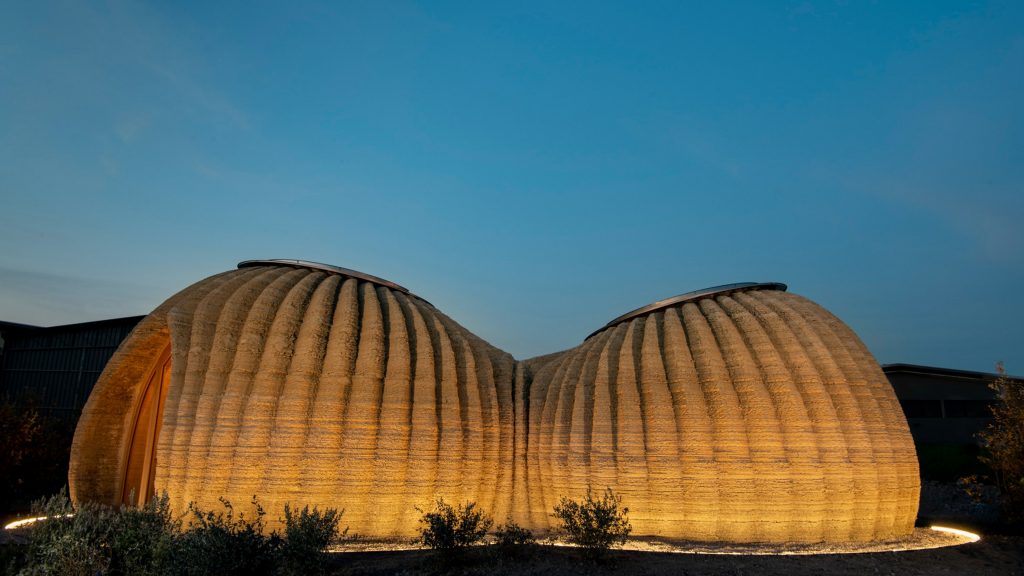
Other than what is 3D-Printing, it is important to look at the main areas where it is useful. Construction and architecture, which are often wasteful professions responsible for about 40% of greenhouse gas emissions, are the two key domains where 3D printing can be beneficial. 3D printing offers the potential to employ cleaner ways of making cement-based goods such as walls, often in significantly shorter durations than traditional building procedures.
The industrial platform is gaining popularity and efficiency day by day and has no intentions to slow down. New industrial research and development are also on the increase, indicating that 3D printing has a promising future.
Please visit and subscribe to our YouTube channel and stay tuned to our videos.























Leave a comment