Artificial Intelligence (AI) emerged in the 1950s when researchers discovered that machines could perform human-like tasks like thinking. Later, in the 1960s, the Department of Defense in the United States funded AI, and labs were established for further development. Researchers noticed that AI benefits many fields, such as space exploration and survival in extreme environments.
Space exploration is the study of the cosmos, which encompasses the entire universe outside Earth. Space is categorized as an extreme environment as it has conditions different from Earth’s. Many factors must be considered to survive in space, and precautions must be taken. Scientists and researchers believe that exploring space and understanding why everything is how it is aids in comprehending the universe’s workings, preparing for potential environmental crises, and fostering adaptable survival skills.

Generally, it is necessary to explore space, much like it is important to explore the ocean, mountains, forests, and deserts. It helps us understand our surroundings and find more resources to improve our everyday lives. As the world continued to develop, scientists and engineers manipulated computers to our advantage and for the world’s greater good. Great minds since the 1950s and 60s helped develop artificial intelligence that not only helps humans complete basic tasks but aids in analyzing problems and coming up with solutions and opportunities that benefit the next generations ahead.
Long ago, humans used to go on space missions alone for the purpose of research. However, artificial intelligence became a trusted companion when going on exploration missions in extreme environments such as space. AI goes beyond human capabilities and helps dive deeper into the cosmos by using advanced computing and algorithms, machine learning, and robotics. It processes astronomical data incredibly quickly and accurately, surpassing any other method. It detects patterns, uncovers concealed connections, and reveals cosmic occurrences that were previously beyond our understanding. AI also provides us with new tools and methodologies for studying and interpreting cosmic phenomena that humans cannot detect.

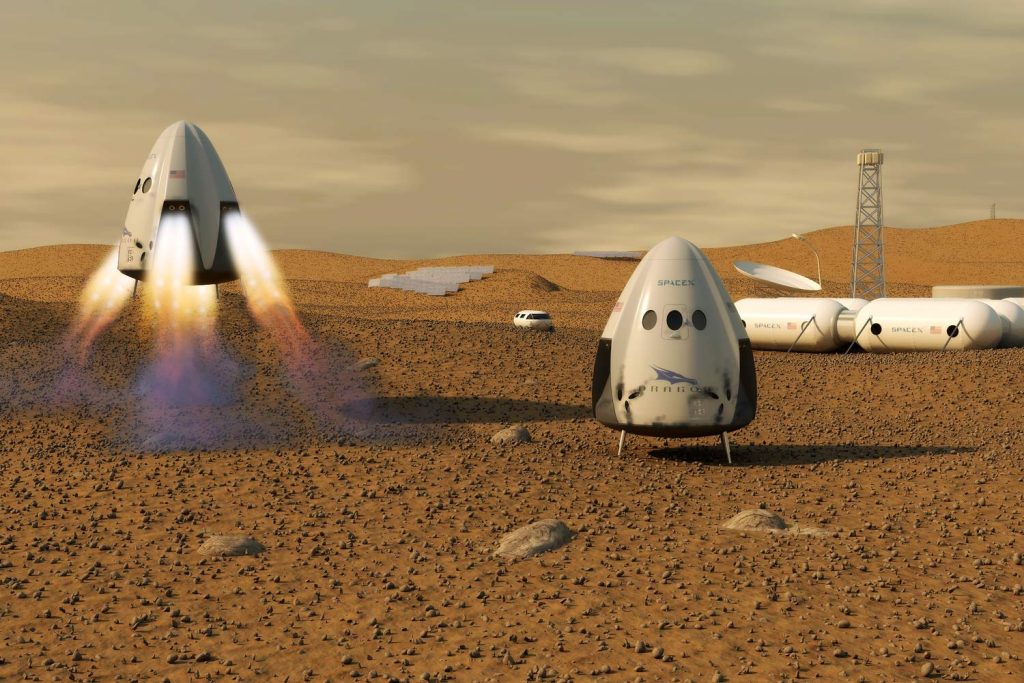
It is well known that the infinite vastness of space is very challenging for humans to study and explore accurately. For this reason, intelligent robotic systems have been aiding in space missions ever since the late 1950s when the first case of artificial intelligence was used, an advanced algorithm to detect any defects onboard the NASA spacecraft. Later, in 1997, artificial intelligence was used to look for and collect samples from the Martian surface. In 2004, intelligent computers were used to identify, collect, and perform experiments on samples. Astronauts, engineers, designers, and many other experts kept testing artificial intelligence in space until research proved that AI could aid in controlling the spacecraft, collecting and analyzing data, and making quick decisions.
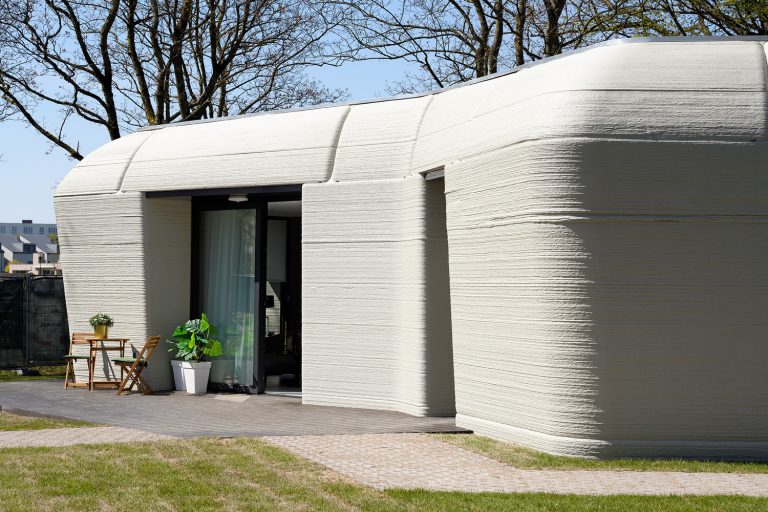
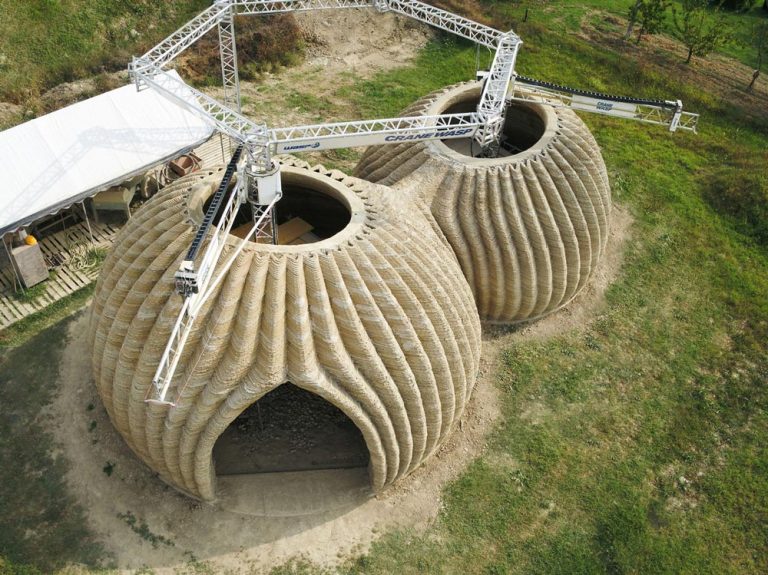
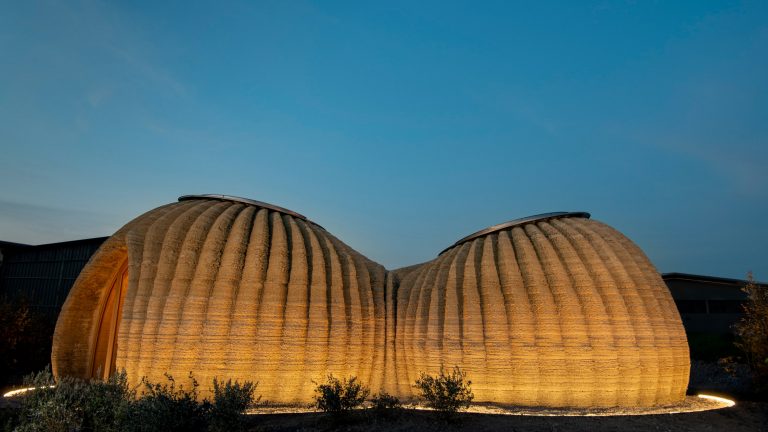
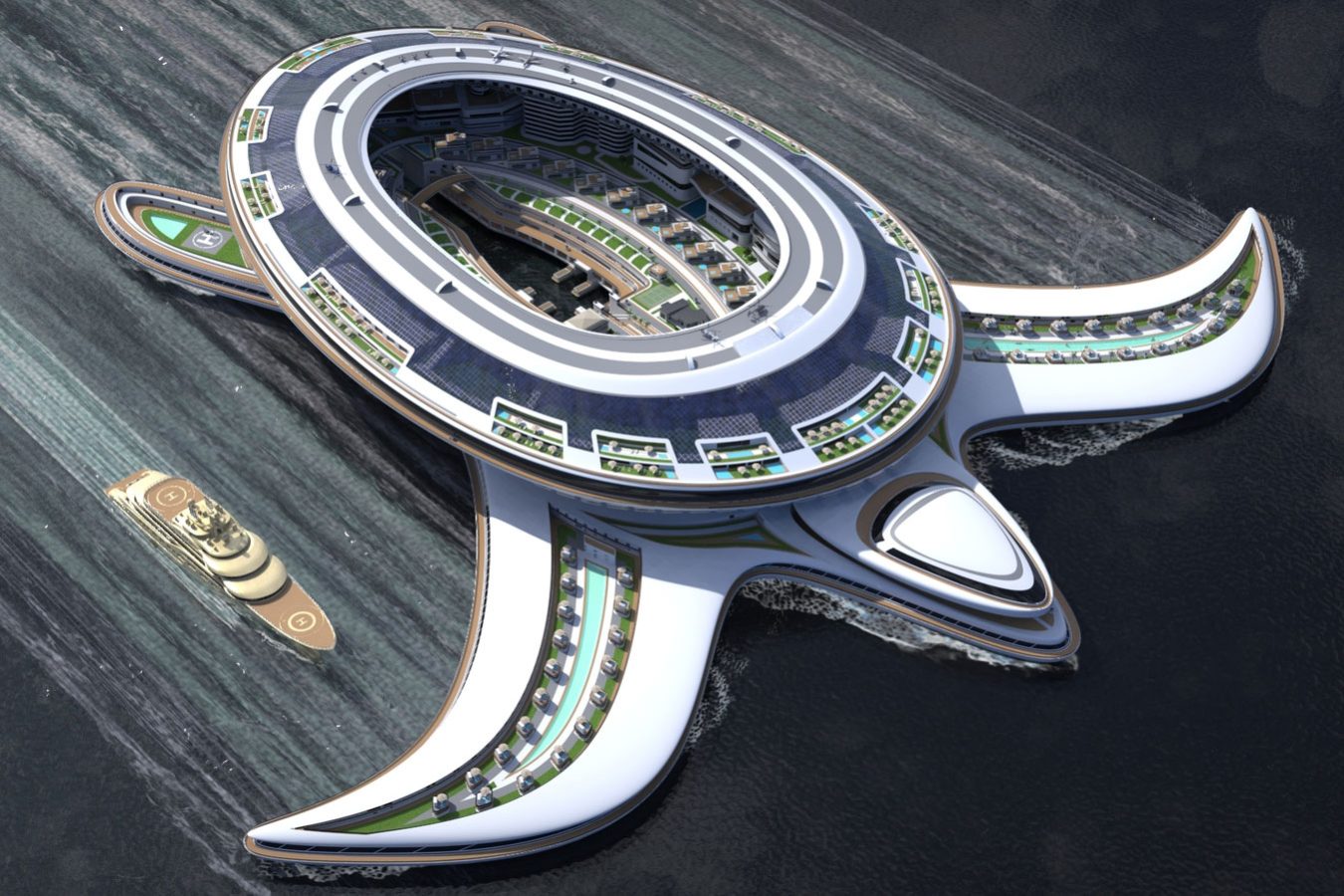
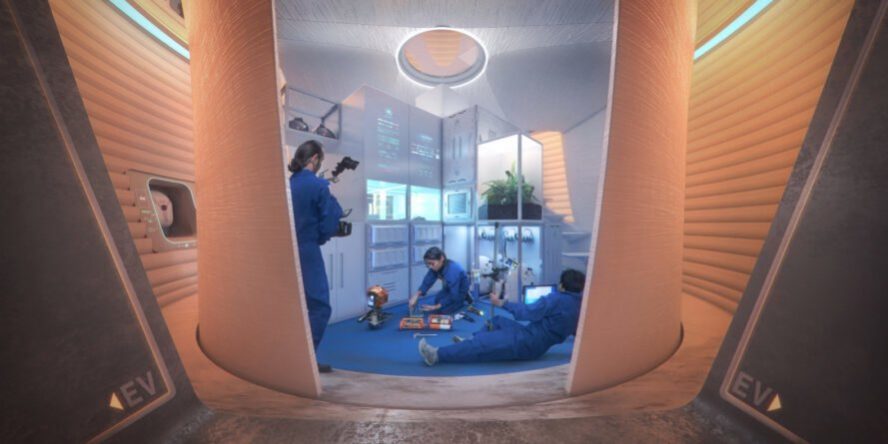
Artificial intelligence is not only beneficial in aiding space missions and research, but it is a technique used in many fields related to space. Scientists and researchers spend years in space studying the cosmos, and for them to survive in the vastness, habitats are designed and created by space architects with the help of artificial intelligence. Advanced algorithms and intelligent technology help space architects design and bring those habitats to life because when designing for extreme environments like space, it is vital to consider many aspects that allow people to survive for a long period of time. Those habitats are expensive and detailed pressurized volumes that mimic the environment on Earth because researchers can’t conduct their studies without them, as space environments are inhospitable for humans.

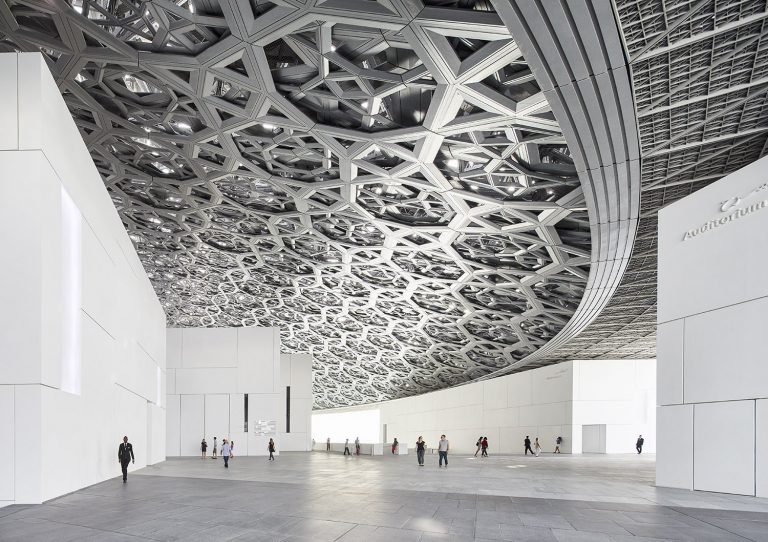
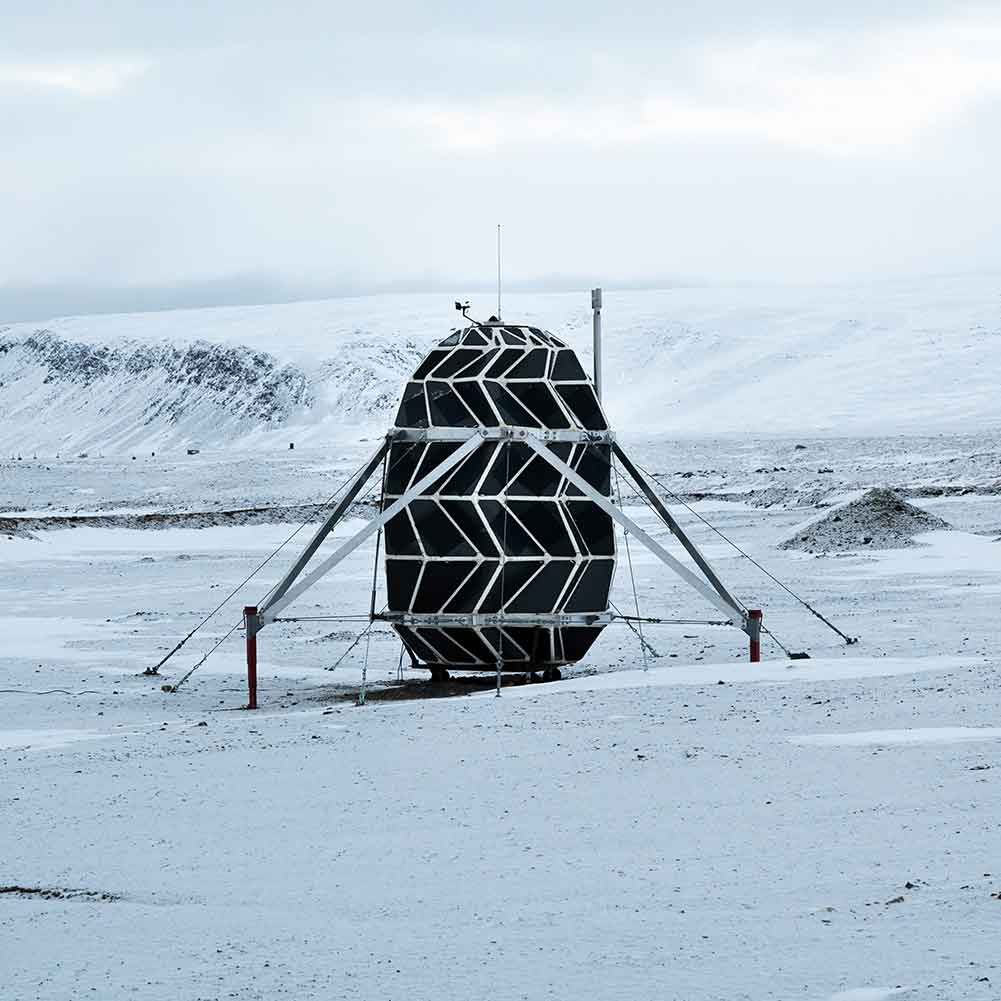
Space architecture is a specialized field focused on designing and constructing living and working spaces for humans in outer space. The environments vary, from space vehicles, which are used for transportation to and from space to support human occupants during their missions, to space stations, which are large structures and habitats where astronauts live and work for extended periods. A famous example is the International Space Station (ISS), where researchers spend most of their time completing their studies; it includes accommodations, laboratories, and operational spaces.
The ISS was originally designed to serve as a space laboratory, but with time and technological advancements, it developed into a home for scientists and researchers, including many other functions necessary for survival. Apart from functionality, it was important for designers to consider human psychology by adding windows to view the outdoor environment and enhance their experience while working for days, months, and possibly years.

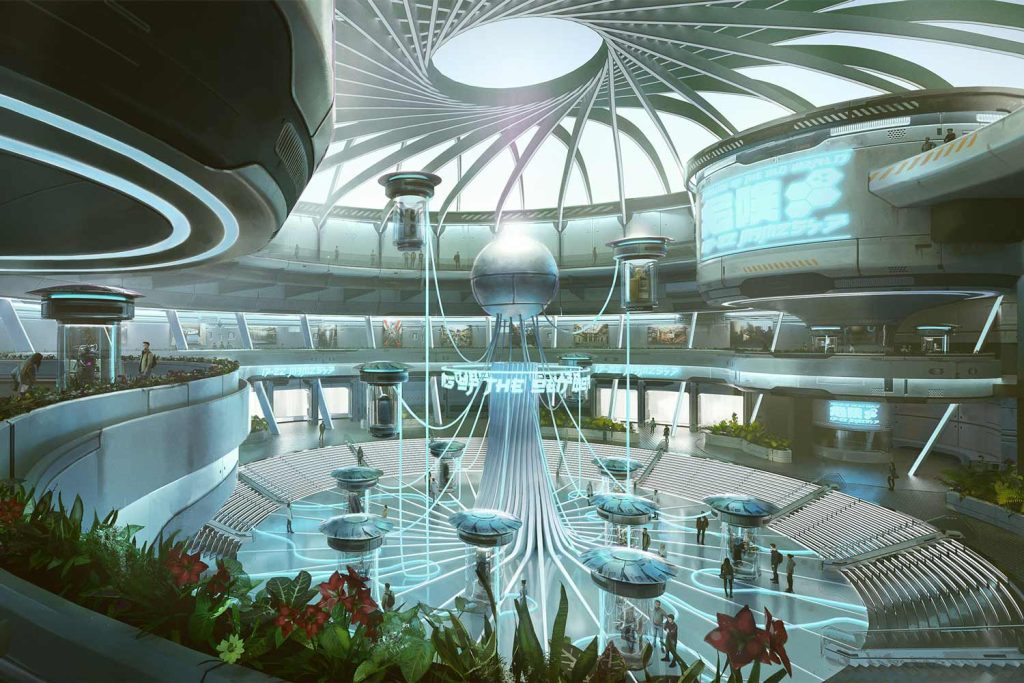
Additionally, habitats are also needed structures or modules that provide a living environment on other celestial bodies such as the Moon or Mars. These living environments must be a means of protection from harsh space conditions while providing essential life support systems. Other types of environments include lunar and planetary bases, which are permanent installations on the Moon or Mars, where humans live and conduct experiments and research.
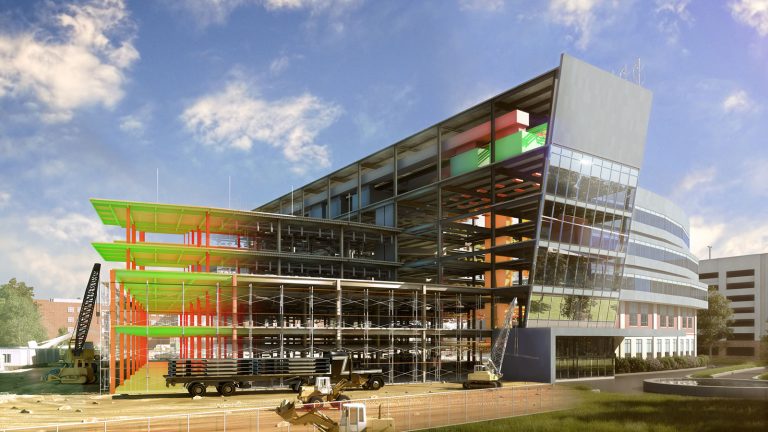
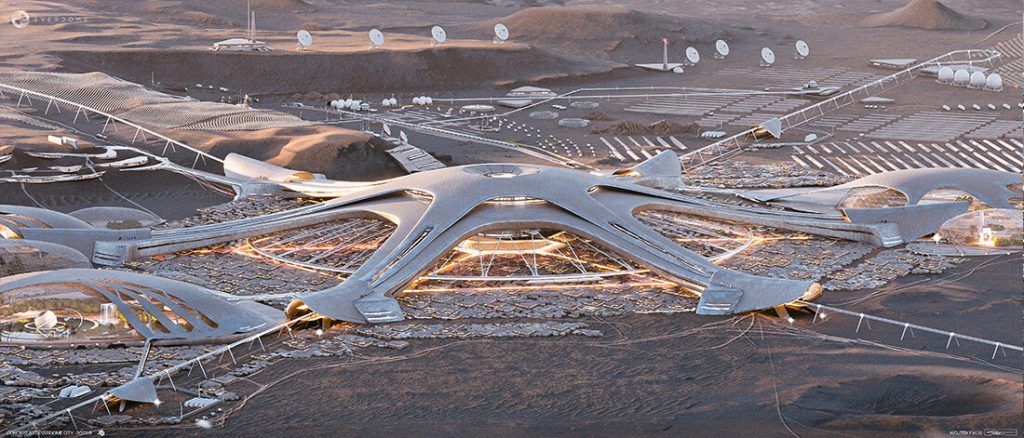
Architects and designers intricately plan these bases to be self-sustaining as much as possible by considering factors such as power generation, water recycling, and food production. Lastly, space architects design e+arth-based facilities on Earth to support space missions. Such facilities include control centers, laboratories, logistic centers, simulation facilities for training astronauts, and test facilities for spacecraft components. Essentially, space architecture, with the help of artificial intelligence along with traditional architectural elements, creates a safe environment for humans to live and work in the unique and challenging conditions of outer space.
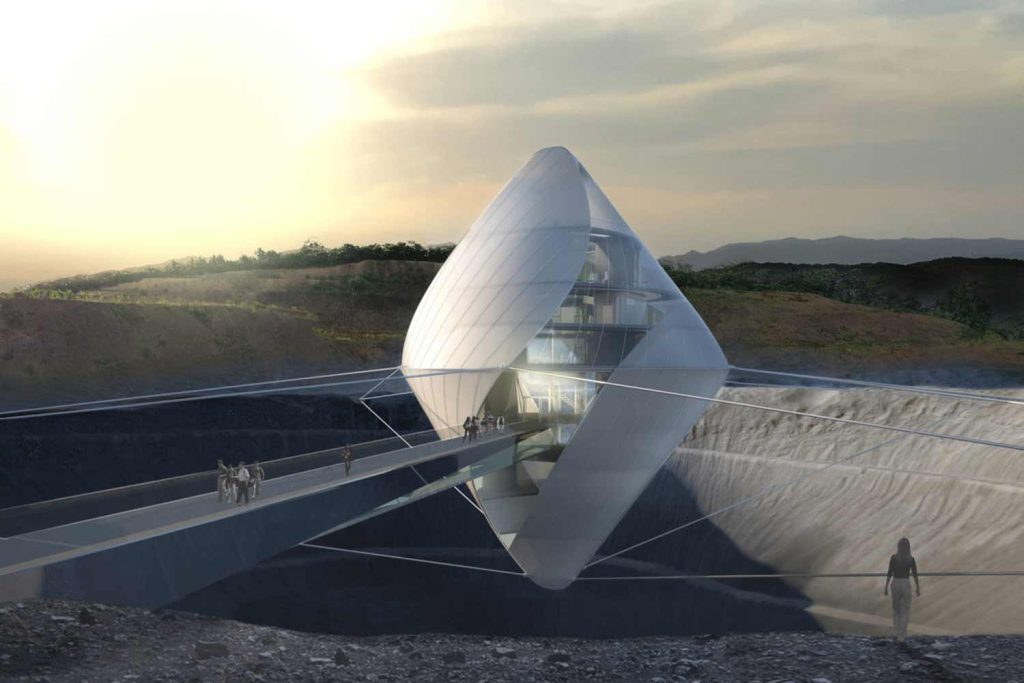
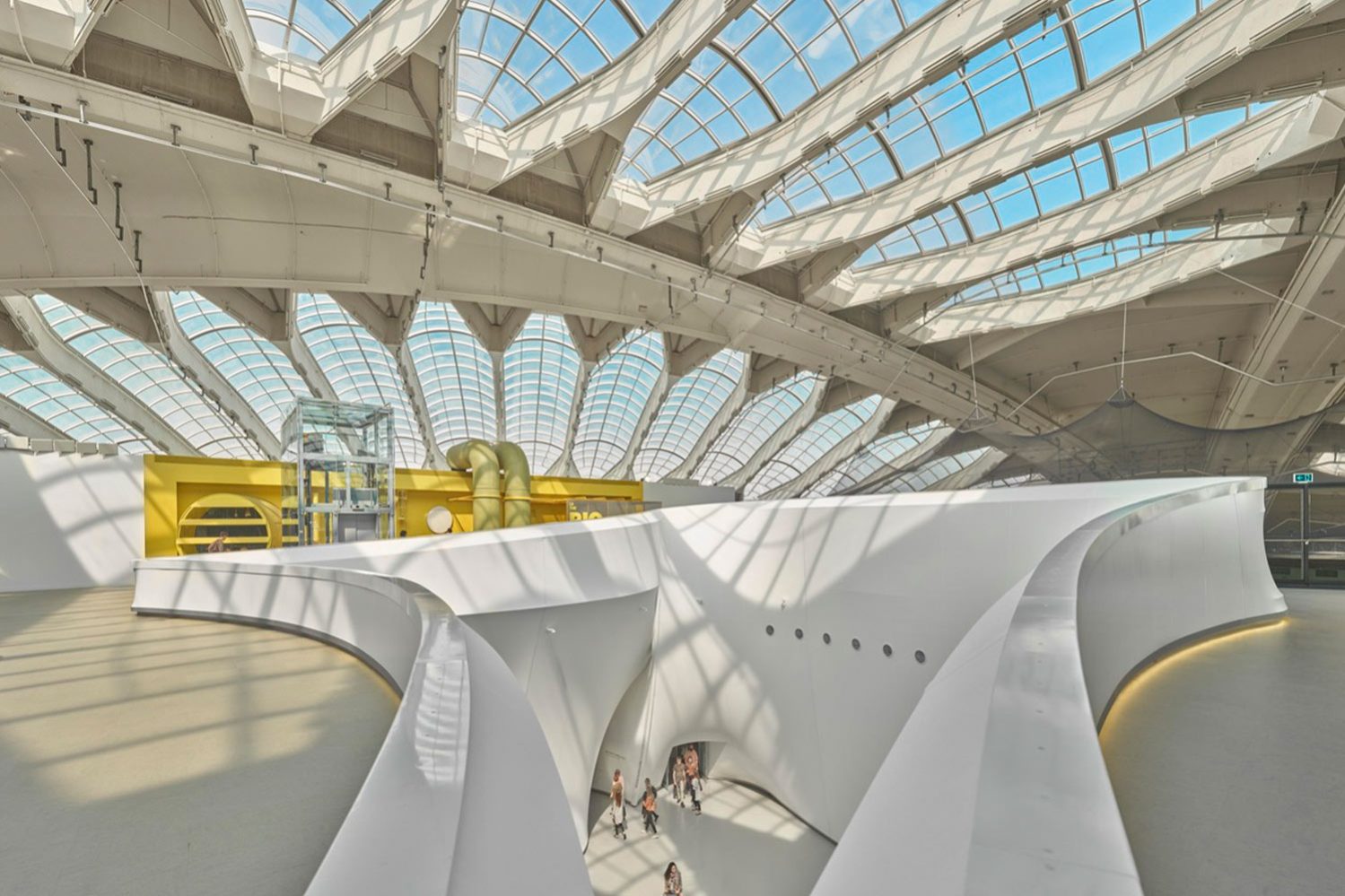
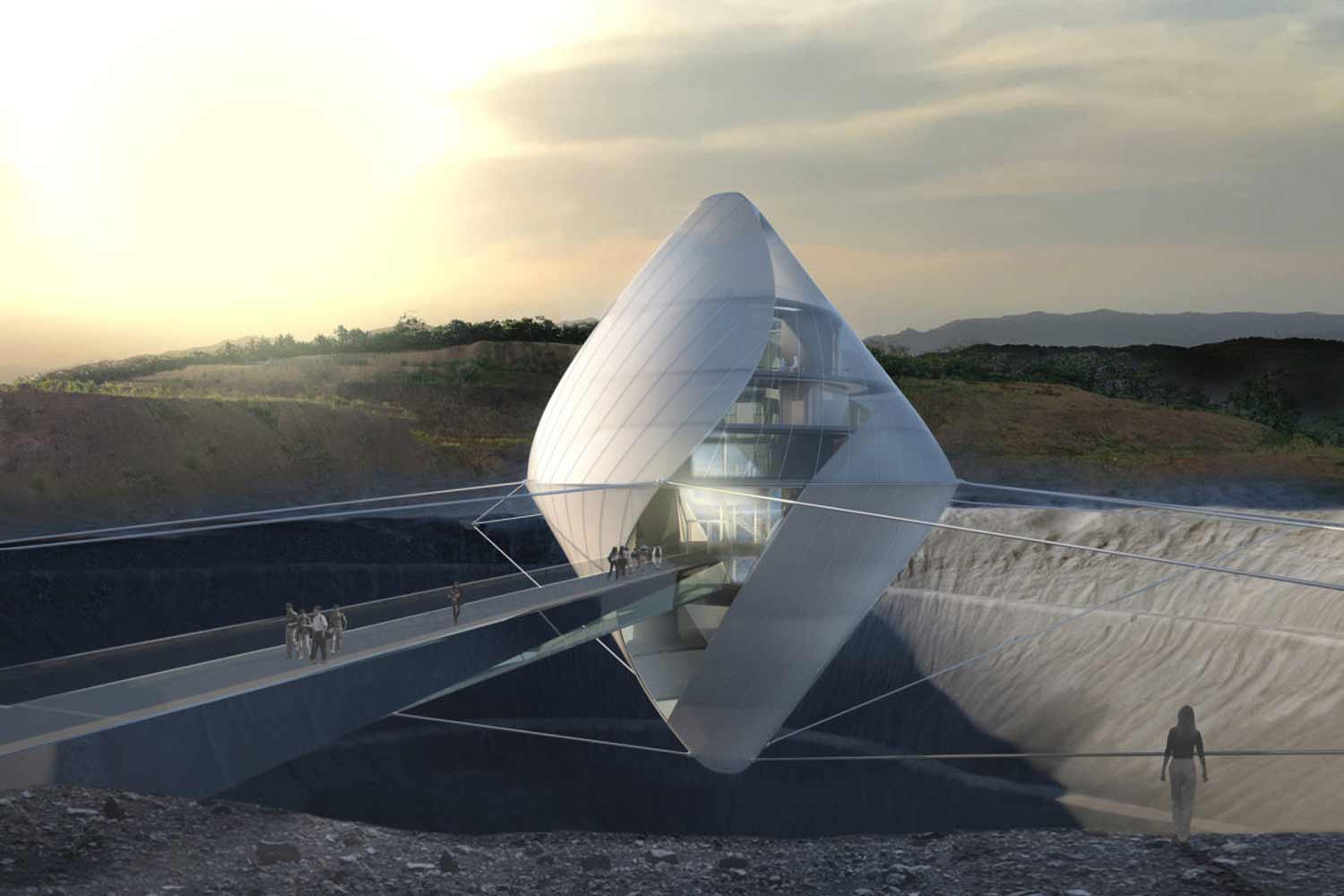
Research explains that technology and artificial intelligence are shaping the future of space exploration. Space architects depend on generative architecture to rapidly create models and simulations of space habitats. This includes everything from optimizing the layout and interior design to identifying and addressing safety concerns. Due to the harsh conditions in space, space architects focus on creating functional designs that can adapt to these environments for humans conducting space travel or living there for research purposes. By employing specific algorithms, artificial intelligence can offer multiple design options for architects and engineers to choose from, minimizing design flaws and increasing the chances of survival on space.
Artificial intelligence not only helps in designing habitats, but it also assists in designing small equipment parts like cars and motorcycle chassis. Essentially, artificial intelligence and generative architecture can analyze data, simulate designs, and optimize outcomes more efficiently. However, Research Engineer Ryan McClelland emphasizes that despite AI being quick, efficient, and a great help for humans in space, ‘the algorithms do need a human eye.’ Meaning, AI can replace human analysis, but it cannot replace human intuition, which always knows better. They believe that this combination can create wide-span structures and entire habitats. AI and space exploration are ongoing studies experiencing trials and errors until today, but they definitely ensure a promising future for space architects.