Artificial Intelligence has become an irresistible force in today’s world, plunging itself into nearly every aspect of human life. Yet, the construction industry is a key area where AI has been blooming lately. As the $10 trillion industry propels itself into faster-paced and digitized contexts, the impact of AI is subverting many traditional methods.
Planning and design
As every architect knows, design is never a linear process. With so many back-and-forth movements in parameters such as dimensions, scale, layout, accessibility, and carbon footprint, AI has the ability to alter these parameters to the specific demands of the user, creating an outcome that maximizes the design potential. In fact, in a survey of over 2000 design professionals, 55% revealed they had already embraced AI or started experimenting with it.
Recent tools include Maket, ARCHITEChTURES, Ark Design AI, Sidewalk Labs, Hypar, Finch, and many more. As these tools continue to use machine learning to analyze thousands of plans, they can be used in the most efficient and cost-effective pattern for the stages of design development.
Site Safety
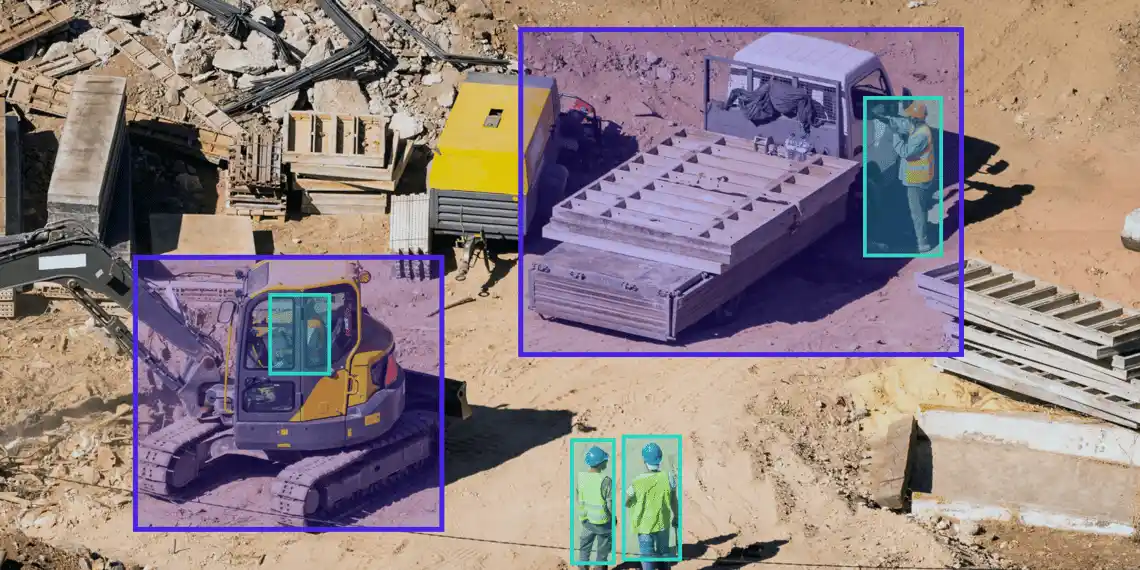
As construction workers are engaged in various tasks such as dealing with heavy machinery, working from heights, and contacting hazardous materials, ensuring the safety of every individual can become a challenge. As a solution, AI-powered cameras come into play. These cameras have the ability to continuously scan the site and use image recognition algorithms to detect potential safety hazards.
For example, the company Basic AI uses this technology to identify when a worker forgets to wear a helmet and immediately alert the site manager. The technology can also detect unsafe scaffoldings and issues with waterlogging and analyze data from past projects to identify patterns and predict potential safety issues.
Maintenance
Another potential problem on construction sites is unexpected machinery breakdowns. These types of failures can cause significant project delays and cost overruns, while equipment like cranes and bulldozers are crucial to the construction process. An example of a company that applies AI-driven predictive maintenance technology is Caterpillar. This company utilizes AI algorithms that analyze data from sensors installed on machinery to predict when equipment might fail or require maintenance.
As data on temperature, vibration, and sound are gathered, AI analyzes the machinery’s health to identify anomalies, such as unusual vibration patterns in the engine. As a result, traditional maintenance approaches become more efficient and reliable strategies.
Risk assessment
A construction risk assessment aims to identify dangerous factors in construction projects. We can now use AI predictive analytics to help reduce those risks. Tools like Construction IQ are able to prioritize problems and understand risks, such as potential consequences, if a concern is not handled.
Companies such as Autodesk use Construction IQ to gather data from programs such as BIM 360 Field, a cloud-based construction field management software that keeps the office and field teams in sync. They then apply analytical techniques and machine learning to transform that data into actionable insights. The daily risk assessment feature uses algorithms to sort through thousands of project issues and classifies issues as “high risk” if they involve the risk of a fall, a water hazard, or an overdue safety inspection.
Sustainability
With the current climate crisis and the intense carbon footprint of building materials, 38% of global energy consumption is correlated to the construction industry. In response to this, AI technology offers novel approaches, such as using energy modeling software to simulate a building’s energy use intensity, smart grid technologies to adjust lighting and HVAC systems, choosing sustainable materials based on their lifecycle, and managing waste and recycling materials to maximize the sustainable construction cycle.
The example companies include Pello, which utilizes AI-powered sensors that monitor bin fill levels, track container locations, and show contaminations; BuildingIQ, which uses a cloud-based software platform called predictive energy optimization that can reduce HVAC energy consumption by 10–25%; and CarbonCure, which uses to AI to analyze data from concrete production processes and injects (CO?) into concrete during mixing, where the CO? becomes chemically converted into a mineral.
Automation
Another crucial aspect where AI comes into play is the usage of autonomous vehicles in construction. With the help of machine learning, AI algorithms can analyze data from LiDAR and GPS sensors to create meticulous maps of construction sites and detect obstacles, while equipment like excavators and bulldozers can be autonomously controlled. Example companies include Built Robotics, which offers a fully autonomous excavator equipped with 360° smart cameras, and Caterpillar, with their autonomous mining trucks and bulldozers manufactured since 1994.
Despite all of the benefits we’ve concluded, integrating AI into the industry comes with several challenges. Primary concerns include the replacement of human workers, which led to job losses for construction workers, as nearly 65,000 people were cut from their jobs at U.S. companies in April 2024, reliability of AI, as the technology is not infallible and has the potential to compromise the safety of construction workers, and lastly the level of privacy and security of the analyzed data that is potentially open to cyber-attacks from outside sources. Considering these setbacks, integrating AI into the industry still offers many exciting possibilities, yet how far it will take us or whether it will completely replace human labor is certainly open for discussion.
 In this article:
show
In this article:
show





















Leave a comment