Researchers at ETH Zurich have done a new robotic additive manufacturing method to foster sustainable construction through “impact printing.” This new, innovative process utilizes earth-based materials such as clay and excavated earth-very inexpensive, abundant, and environmentally friendly-alternatives to traditional cement-based building methods.
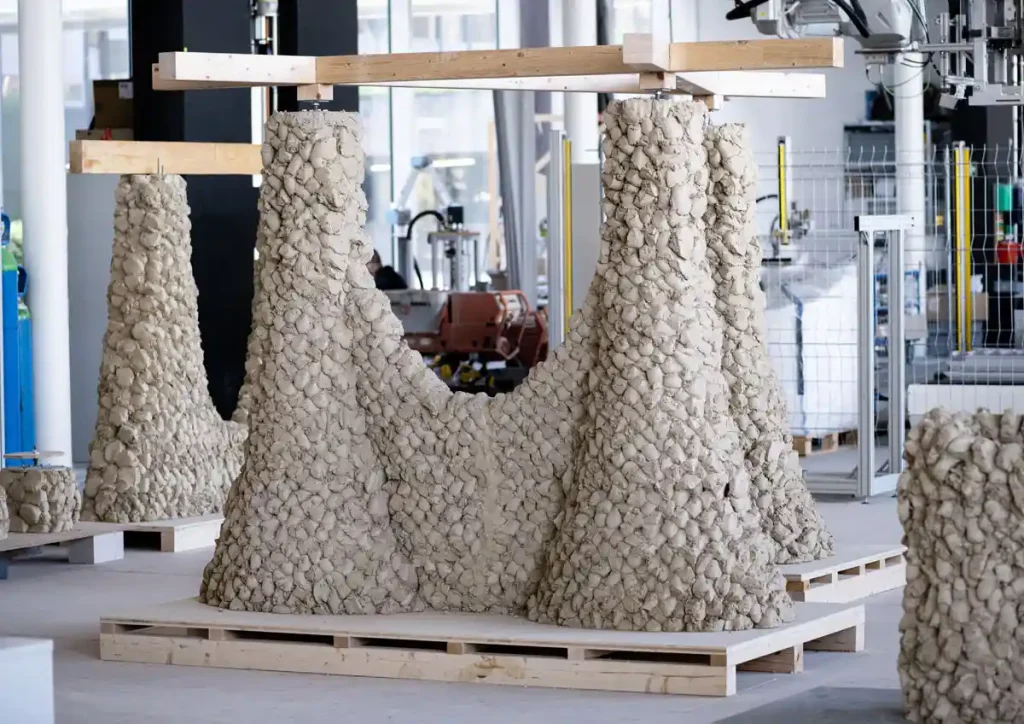
The impact printing overcomes the labor-intensive and costly nature of the current earth-based construction techniques by adopting construction robots shooting material from above, developing walls gradually upon impact. Such materials bond together, often with just a few additives, to form a strong, stable structure, without the need to stop and wait for the material to solidify, as is the case in concrete 3D printing.
The impact printing method can deposit dense materials at huge velocities, say up to 10 meters a second for strong bonding between the layers. It does not seem entirely dependent on additives, as with typical layer-based 3D printing. That way, it will allow a more stable and efficient construction process.
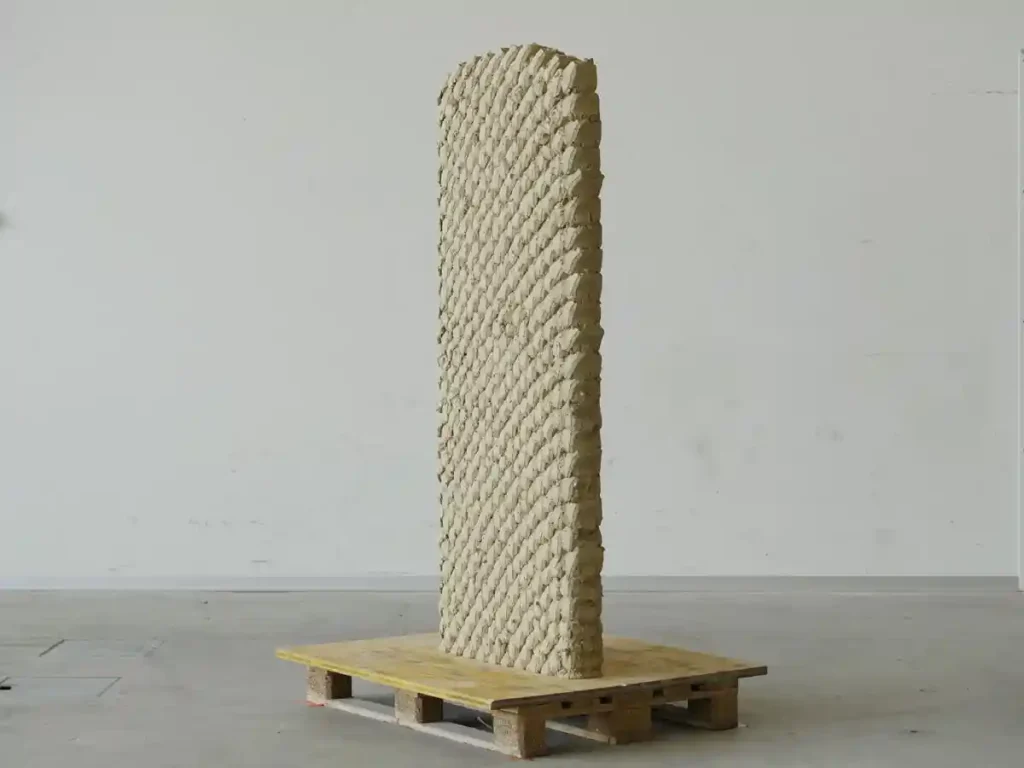
ETH Zurich researchers designed a custom printing tool that could be outfitted on various robotic platforms, including offsite production systems and autonomous legged excavators, for construction in everything from vertically constrained urban areas to remote, natural areas. Indeed, the robotic system has already been used to build walls as high as 3 meters-or nearly 10 feet-to demonstrate its ability to undertake major building projects.
ETH Zurich’s team developed the method from scratch, using only circular, low-carbon materials to keep environmental impact as low as possible. The earth-based mixture used in construction consists basically of local, sustainable materials with only a few additives.
In collaboration with Eberhard Unternehmungen, one of the leading companies working on circular construction methods, the researchers want to be able to extend this technology even more into other materials and applications in the future. Impact printing can revolutionize the building industry as it holds the potential for speeding up processes, being ‘greener’, and making the process less expensive when constructing a structure with a minimal environmental footprint.




















Leave a comment