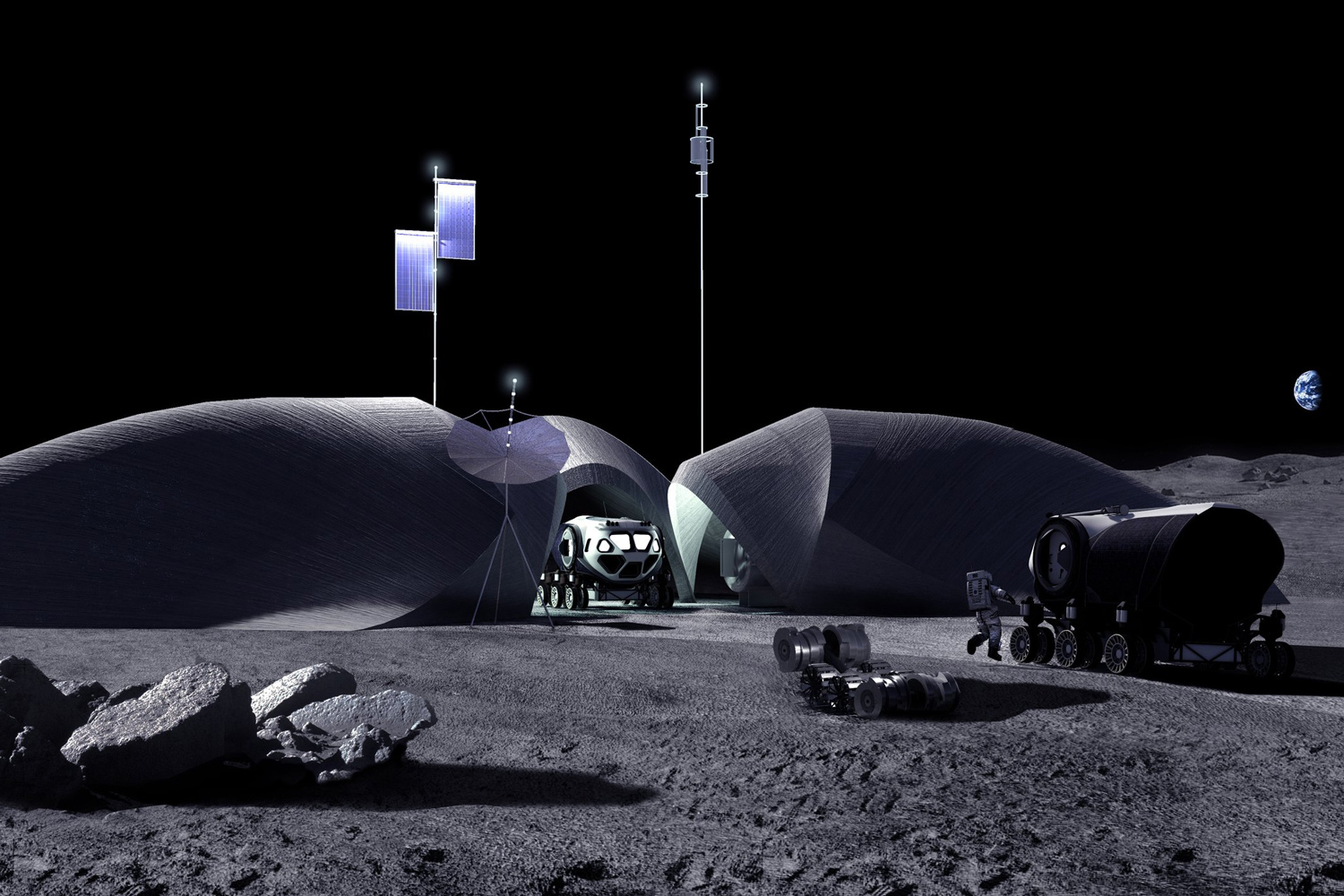
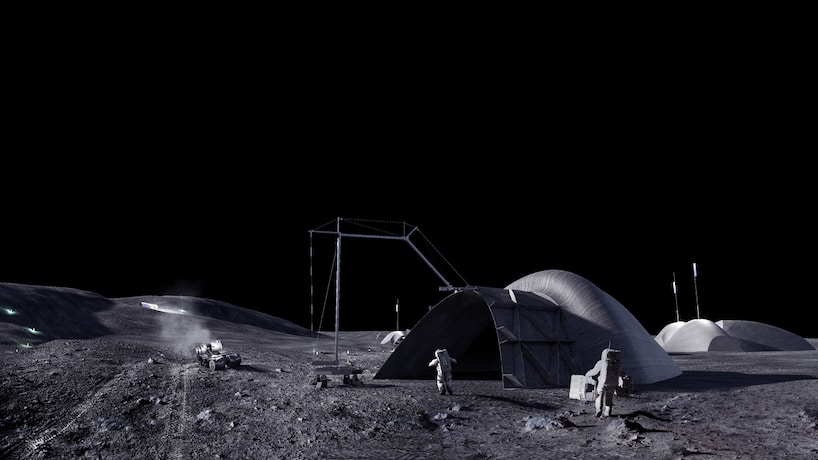
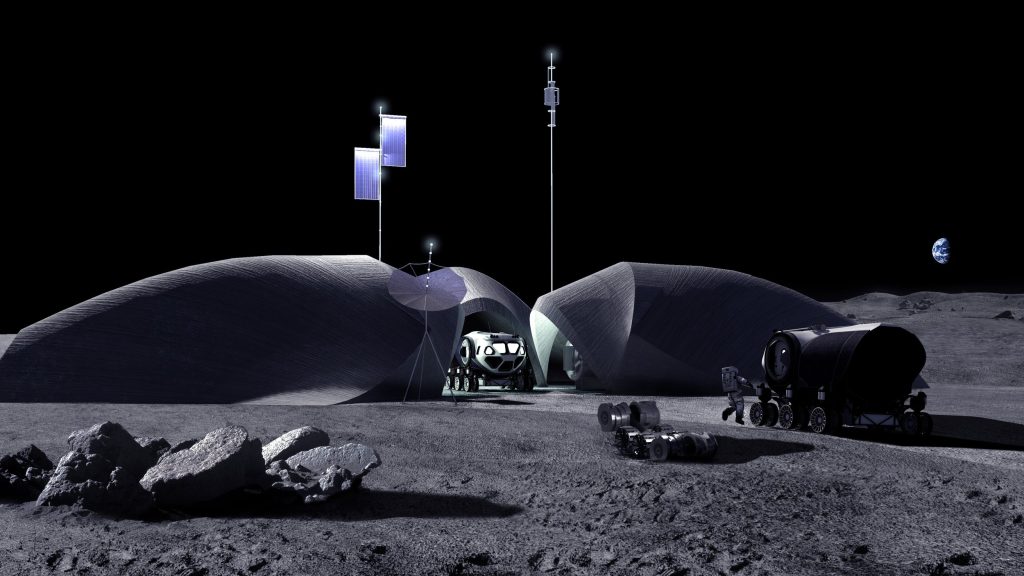
NASA and AI Space Factory developed LINA (Lunar Infrastructure Asset) as part of the Relevant Environment Additive Construction Technology (REACT).
The primary function of LINA is to protect astronauts and critical mission assets from galactic cosmic radiation exposure, solar particle events, moonquakes, micrometeoroid impacts, lunar dust contamination, and cryogenic conditions experienced during the lunar night and designed with a life expectancy of at least 50 years.
LINA’s ultra-thin shell is designed to support a barrier protection regolith overburden 2.7 meters thick. As a result, a lightweight, mass-optimized structure protects against radiation and the harsh lunar environment. Also, LINA will be 3D printed with a high-performance mixture of native lunar regolith and Earth-sourced polymer binder.
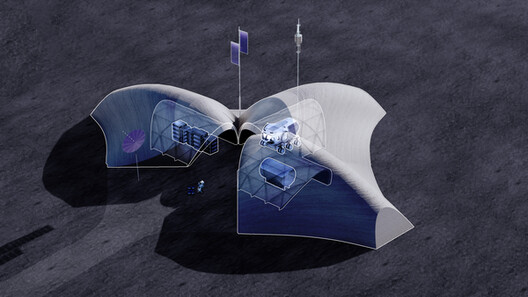

LINA is large enough to shelter a pressurized, manned rover like the Space Exploration Vehicle, as well as telecommunication and habitation modules. The structure’s design incorporates three distinct units that share a common courtyard and incorporate a photovoltaic tree to directly capture and harvest solar energy.
Each unit has a floor area of 75 square meters, a central staging area of 90 square meters, and a 3D-printed shell measuring 8 meters by 9.4 meters with a height clearance of 5 meters.
The Artemis Mission will send astronauts to the Lunar South Pole within the next decade, a region known as “The Peak of Eternal Light.”
“LINA is our design of a Lunar outpost which is both adaptive and visually sensitive to the Lunar environment. As we realize this long-lived imagination of expanding civilization to Earth’s one and only natural satellite, we are also mindful of exploring the moon in a sustainable way that minimizes the human disturbance. To achieve this goal, SpaceFactory – in partnership with NASA – is developing technologies for in-situ lunar surface construction within the timeframe of the Artemis Mission: humankind’s return to the Moon.” stated AI Space Factory.




















Leave a comment