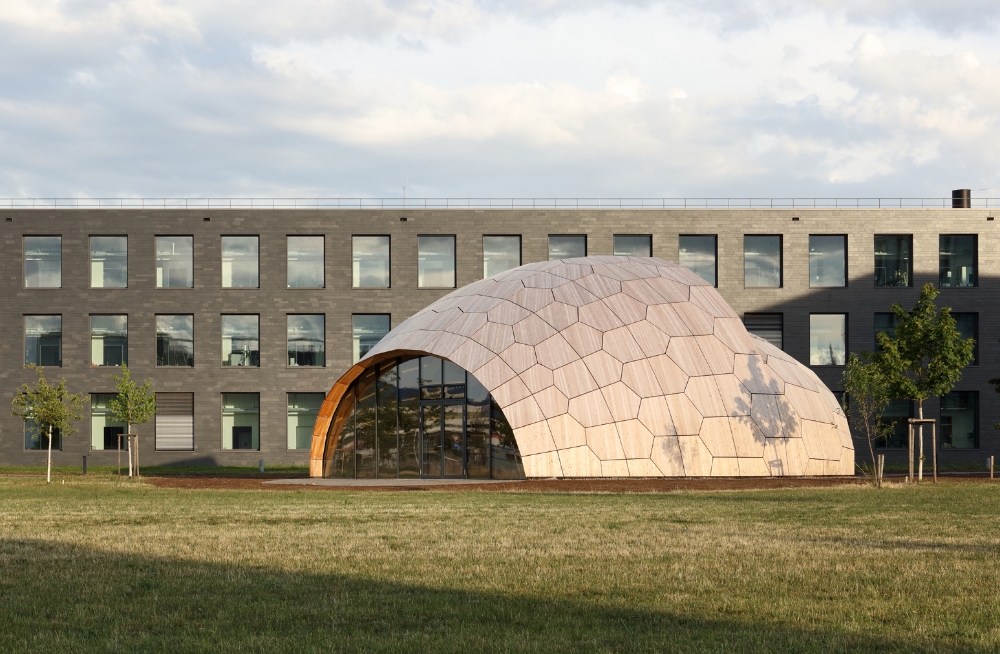
At the FIT Freiburg Centre for Interactive Materials and Bioinspired Technologies, the livMatS Biomimetic Shell is a cutting-edge research structure. The expansive space seamlessly blends into the rest of the campus and acts as an architectural incubator for creating creative, cross-disciplinary research ideas. Simultaneously, the building is a research project involving two Clusters of Excellence, Integrative Computational Design and Construction for Architecture (IntCDC) at the University of Stuttgart and Living, Adaptive, and Energy-autonomous Materials Systems (livMatS) at the University of Freiburg, both of which are investigating an integrative approach to design and construction for sustainable architecture.
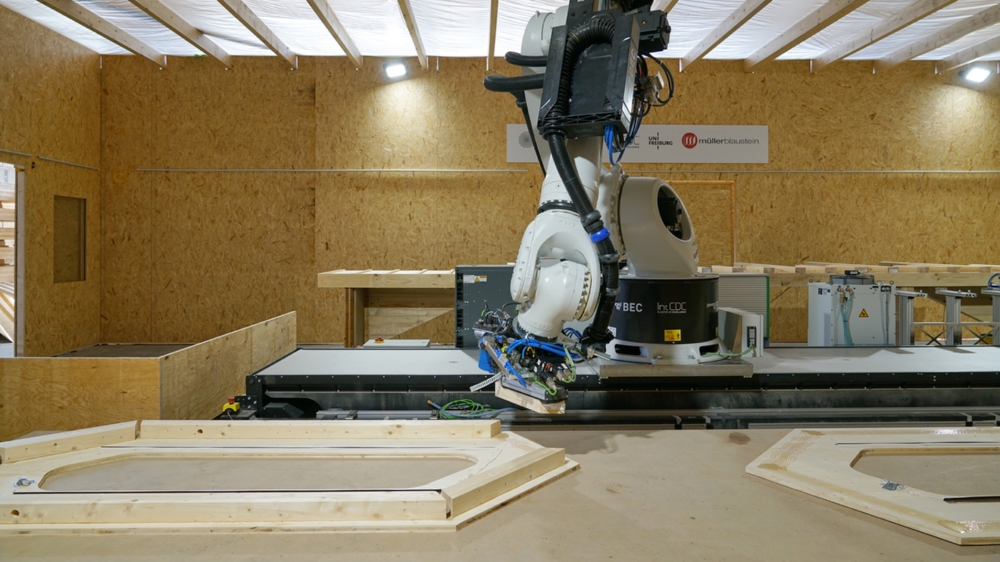
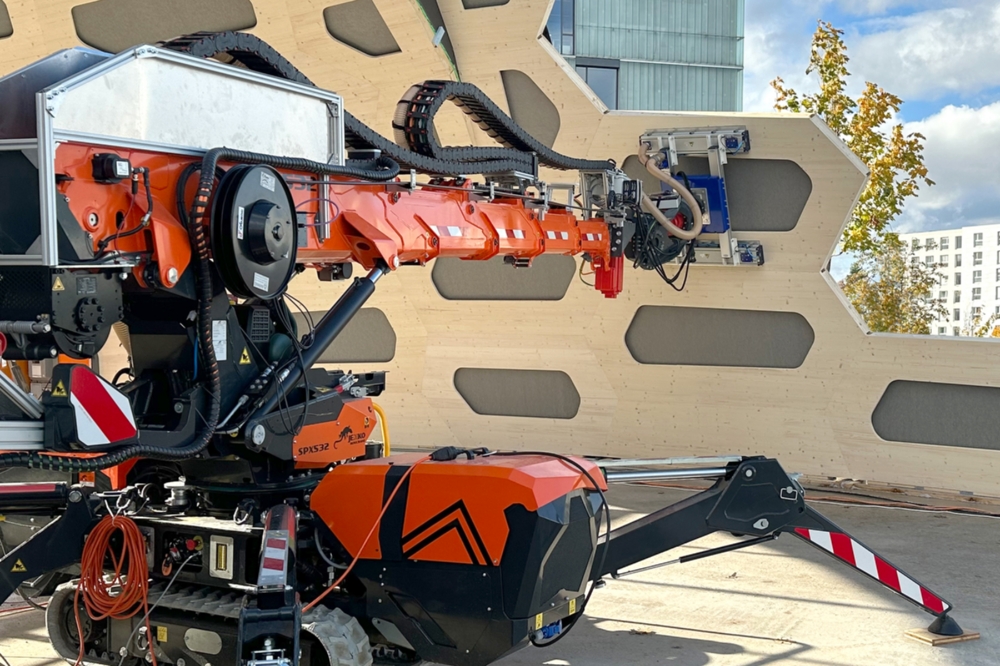
The structure of LivMatS combines the various research philosophies of the two Excellence Clusters to produce an architectural synthesis. The FIT Biomimetic Shell decreases the entire life cycle impact of a standard timber building by 50%. The unique and environmentally conscious segmented timber shell construction is completely deconstructible and reusable. It is made possible by integrating computational design methodologies, robotic prefabrication, automated building methods, and unique kinds of interaction between humans and machines in timber construction.
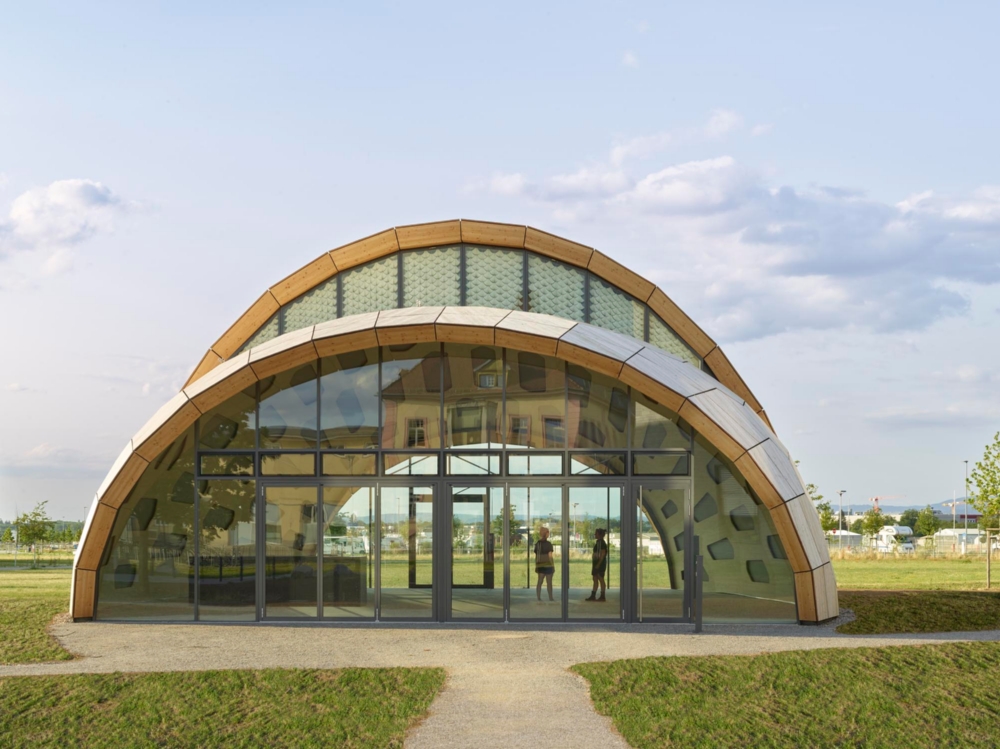
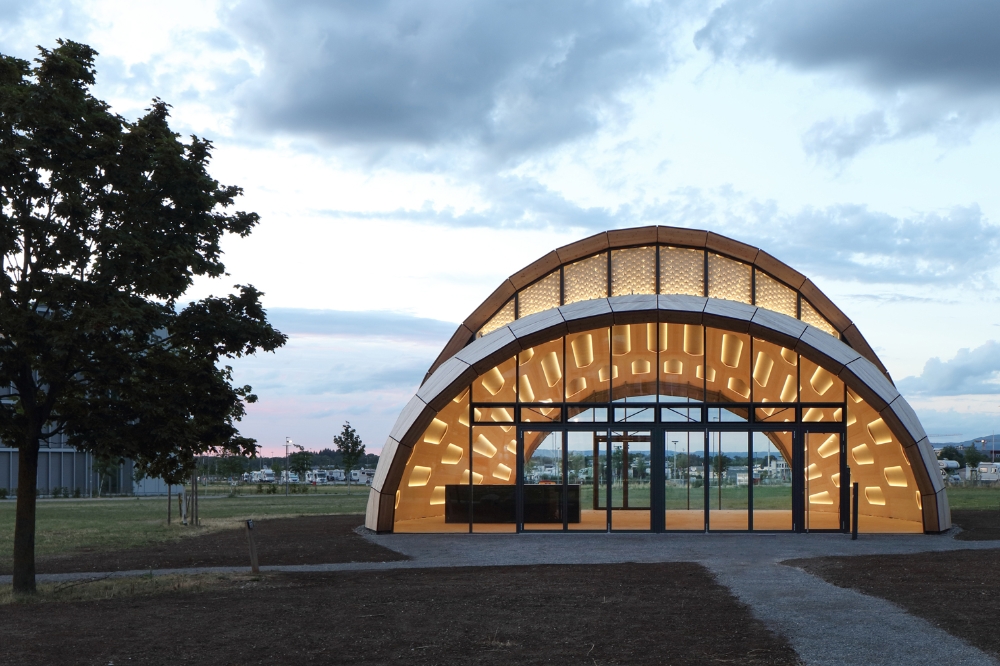
The “Solar Gate” is a big skylight integrated into the wood shell and helps control the inside environment with the help of a biomimetic, energy-autonomous shade system manufactured using 4D printing technology. This, along with an activated floor slab of recycled concrete, allows for year-round comfort with minimum building services. The final product is an eloquent flexible space and architecture that demonstrates alternate paths for sustainable building, as well as a platform for future study.
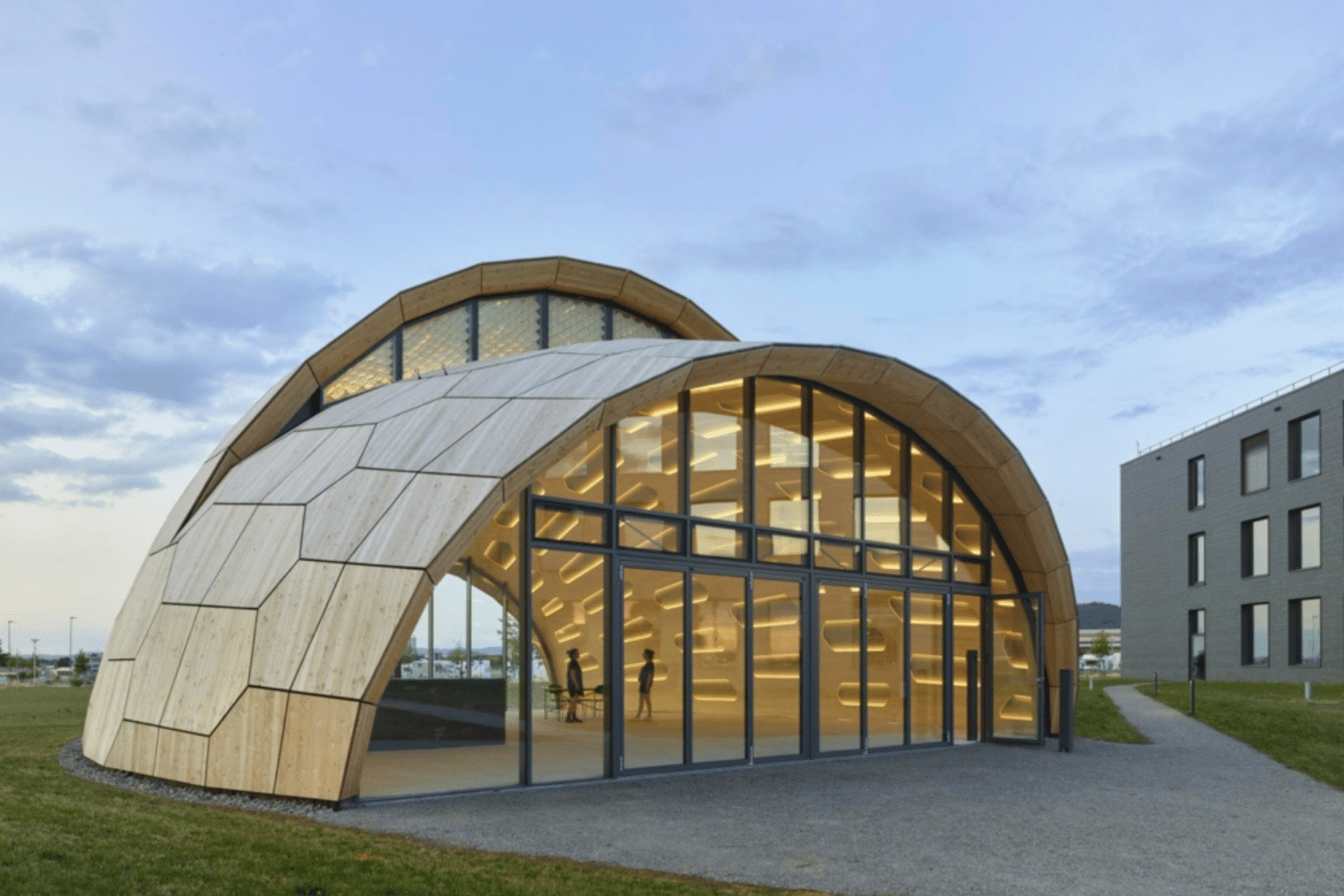
The livMatS Biomimetic Shell is an expansion of the University of Freiburg’s FIT Freiburg Centre for Interactive Materials and Bioinspired Technologies. It allows for the creation of multidisciplinary research concepts. The building is positioned independently on campus as a location for unfettered thought and offers an effortless connection to the surrounding nature with a significantly opening façade.
The outer layer of a structure was developed around the morphological concepts of sea urchin plate skeletons. The revolutionary timber structure spans a floor area of 200m2 and is made up of 127 distinct hollow cassettes connected by cross-screwed joints. When constructed, the wood shell’s curving geometry acts as a form-active structure with a free span of 16 meters and a weight of only 27 kg/m2 of the shell surface. The construction principle provides the distinction of every structural part as well as the reusability of the overall building structure.
The top and bottom layers of the three-layer spruce boards, as well as the spruce edge beams, make up the hollow cassettes, which are put together as building modules. The extra effort required in design and execution for this load-adapted and geometrically distinct construction, which would normally make it expensive, can be made up for by integrative computational design techniques, robotic fabrication, and automated assembly, resulting in a substantial decrease in consumption of resources and environmental footprint.
The livMatS Biomimetic Shell’s comfort strategy is the product of computerized modeling of numerous influencing elements included in the design in order to use the least amount of technical equipment and operational energy possible. The building’s placement and orientation on the location were selected so that the adjacent buildings shed barely any shadow on it on cold days. This enables solar gains to be captured via the massive, south-facing skylight. The timber shell itself is insulated with wood fibers. In the winter, a thermally activated floor slab constructed of recycled concrete that works with minimal flow temperatures from nearby geothermal energy ensures thermal indoor comfort. Simultaneously, large heat loads caused by solar input are avoided in summer.
The livMatS Biomimetic Shell at the FIT Freiburg Centre for Interactive Materials and Bioinspired Technologies stands as an extraordinary testament to sustainable architecture and multidisciplinary research. By integrating the philosophies of two Excellence Clusters, this cutting-edge structure showcases the power of innovative design methodologies and advanced construction techniques. Its deconstructible and reusable timber shell, along with energy-autonomous systems and 4D printing technology, reduce the life cycle impact by 50% and exemplify a harmonious blend of human-machine interaction. Through its eloquent flexibility and sustainable principles, the Biomimetic Shell offers a promising platform for future advancements in the pursuit of environmentally conscious architecture.
Project Info
Project Partners:
Cluster of Excellence IntCDC – Integrative Computational Design and Construction for Architecture, University of Stuttgart.
ICD Institute for Computational Design and Construction
Prof. Achim Menges, Felix Amtsberg, Monika Göbel, Hans Jakob Wagner, Laura Kiesewetter, Nils Opgenorth, Christoph Schlopschnat, Tim Stark, Simon Treml, Xiliu Yang (Biomimetic Shell); Dylan Wood, Tiffany Cheng, Ekin Sila Sahin, Yasaman Tahouni (Solar Gate)
ITKE Institute for Building Structures and Structural Design
Prof. Dr. Jan Knippers, Simon Bechert
Cluster of Excellence LivMatS – Living, Adaptive and Energy-autonomous Materials Systems, Albert-Ludwigs-Universitat Freiburg
Prof. Dr. Jürgen Ruhe, Prof. Dr. Thomas Speck, Prof. Dr. Anna Fischer
Müllerblaustein HolzBauWerke GmbH, Blaustein
Jochen Friedel, Johannes Groner, Daniel Gold
Research Partners:
Cluster of Excellence IntCDC – Integrative Computational Design and Construction for Architecture, University of Stuttgart.
ISYS Institute for System Dynamics
Prof. Dr. Oliver Sawodny, Andreas Gienger, Anja Lauer, Sergej Klassen
IIGS Institute for Engineering Geodesy
Prof. Dr. Volker Schwieger, Sahar Abolhasani, Laura Balangé
ICD Architectural Computing, Institute for Computational Design and Construction
Prof. Dr. Thomas Wortmann, Lior Skoury, Max Zorn
IABP Institute for Acoustics and Building Physics
Prof. Dr. Philip Leistner, Roberta di Bari, Rafael Horn
IntCDC Large Scale Construction Laboratory
Dennis Bartl, Sebastian Esser, Sven Hänzka, Hendrik Köhler
Consulting Enginners:
Ferdrich wodtke Planungsgesellschaft mbh
Christian Erdrich
Transsolar Klima Engineering GmbH
Prof. Dr. Thomas Auer, Christian Frenzel
Bauphysik 5
Joachim Seyfried
BEC GmbH
Matthias Buck
Belzner Holmes Light-Design
Thomas Hollubarsch
Further Execution:
Geoconsult Ruppenthal
Vermessungsbüro Nutto
IB Becherer
Klitzke ELT-Plan
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Heinrich Bechert + Partner
FW Glashaus Metallbau GmbH & Co. KG
Moser GmbH & Co. KG
Lösch GmbH & Co. KG Lightning protection construction
Parquet Studio Ganter GmbH & Co. KG
Elektro Mutter GmbH
Rees Sanitary and heating installations
Jakober GmbH
Kiefer & Sohn GmbH
Dirk Pesec
Project Support:
DFG German Research Foundation
Carlisle Construction Materials GmbH
HECO-Schrauben GmbH & Co. KG
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Puren GmbH
Raimund-Beck KG
- 4D-Printed Shading System
- Automated Construction Processes
- Biomimetic Skylight
- Computational Design Methods
- Cyber-Physical Construction
- FIT Freiburg
- GEN
- Geothermal Energy
- Integrative Computational Design
- livMatS Biomimetic Shell
- Resource Efficiency
- Robotic Prefabrication
- Solar Gate
- sustainable architecture
- timber construction
- Weather-Responsive Façades






















Leave a comment