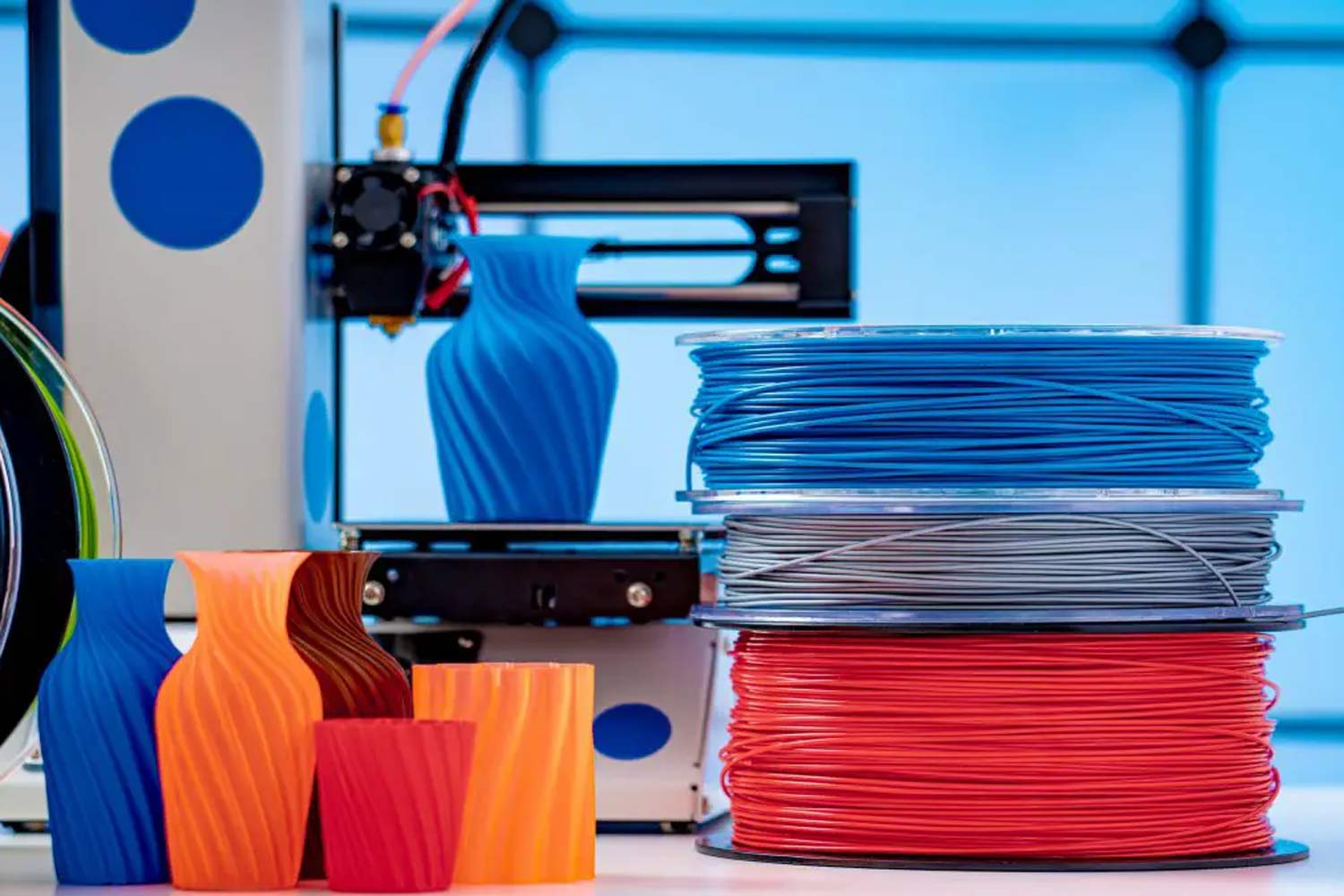
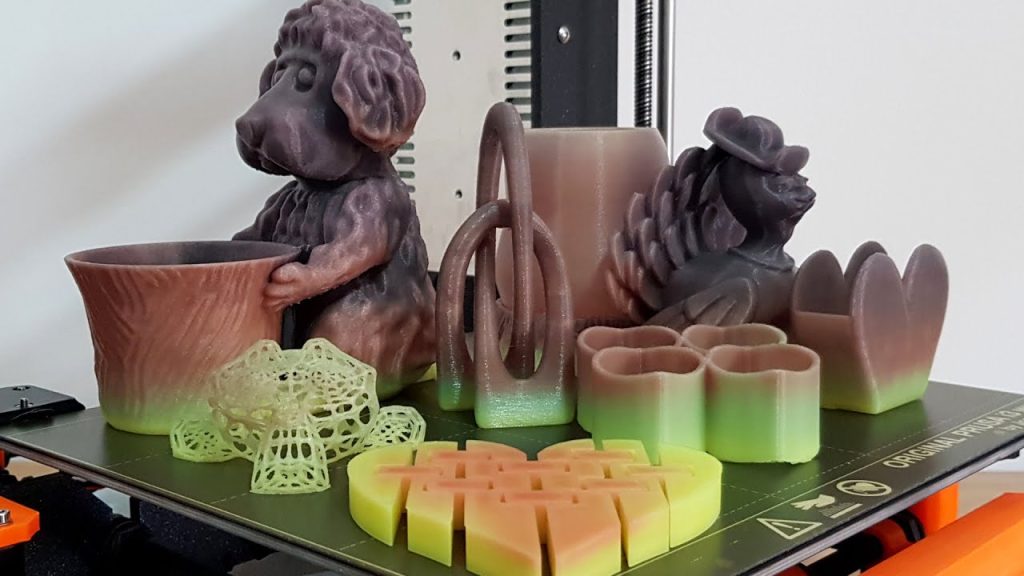
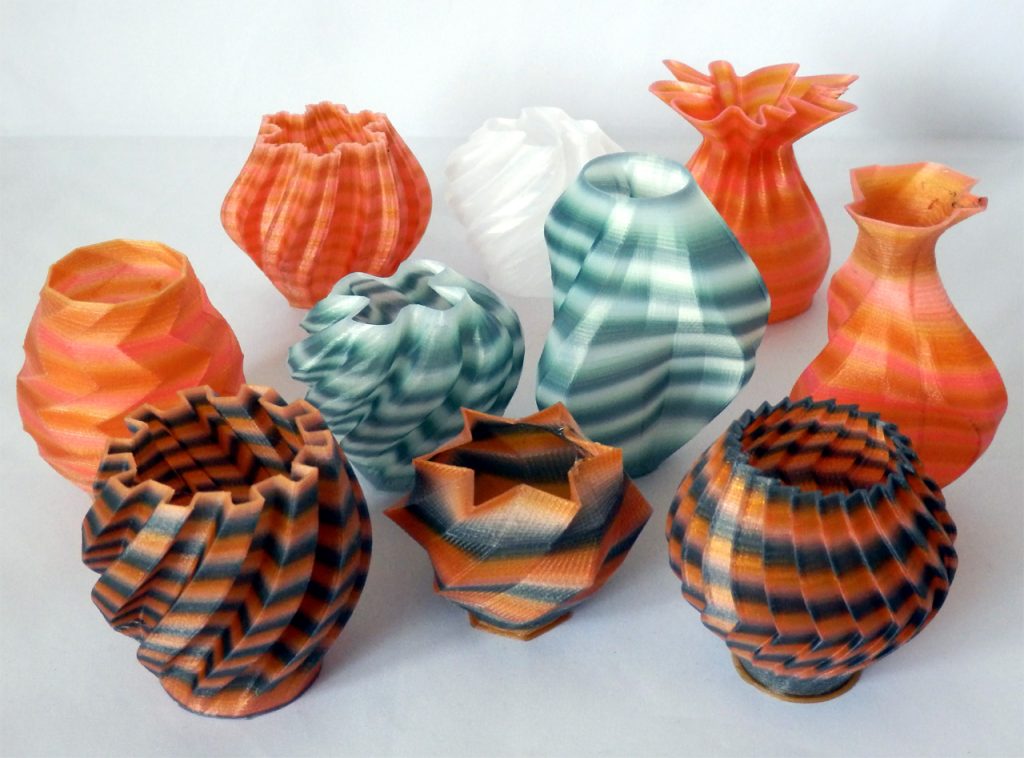
3D printing is the evolving and most commonly evolving method of constructing and designing products and structures. Filaments are available in several colors, textures, and materials applicable for 3D printing in several sectors. Filaments created and designed are innovative, evolving with time some examples such as coffee ground filaments, nylon filaments, color-changing filaments, etc.
Various material filaments are utilized for 3D printing in several sectors such as construction, medicine, and consumer product sector, etc. Here are the 15 Best Filaments utilized for 3D Printing:
1. PLA (Polylactic acid) filament
PLA is a plastic filament commonly utilized for 3D printing applications in various sectors. It is one of the extensively used filaments for 3D printing due to its effortless workability property. It is also referred to as bioplastic sometimes since it is derived from natural sources; corn, sugarcane, etc.
Benefits of PLA filament
- Easy to work with and print
- High tensile strength
- .Biodegradable
- Low-cost filament
Challenges of PLA filament
- .Brittle nature
- Low-temperature resistance
- Precise printing is required since it can string and ooze
2. PETG (Polyethylene terephthalate glycol) filament
PETG is a durable co-polyester(combination) filament used extensively for 3D printing. This plastic filament is known for its recyclable properties (If processed correctly). It is preferred for 3D printing in various sectors primarily due to its durable properties. It has high-strength properties hence it is applicable for various sectors such as medicine, jewelry, engineering pieces, etc.
Benefits of PETG Filament
- High durability
- High tensile strength
- Great chemical resistance
- No odor was produced in the printing process
Challenges of PETG Filament
- Non-Biodegradable
- Slow printing process
- .Bad support material for construction
3. PC (Polycarbonate) filament
PC (Polycarbonate) filament is a strong thermoplastic filament utilized in several engineering sectors that require surviving tough conditions and situations. PC filament is a highly durable material among other filament materials.
Benefits of PC (Polycarbonate) filament
- High tensile strength
- High-temperature resistance
- Good electric insulation property
Challenges of PC (Polycarbonate) filament
- High nozzle and bed temperature
- A separation layer is recommended to be applied
- High warping (Especially – Larger 3D printed products)
- Highly Hygroscopic (Heat bed is required during printing)
4. Metal filament
Metal Filaments are standard plastic filaments (PLA Commonly used) with different metal infusions to create various metal filaments. These metal filaments (steel, copper, aluminum, bronze, iron, etc) have various applications in sectors since are stronger than traditional material filaments.
Benefits of metal filament
- Strong filament type
- Aesthetic finished products
- Low-cost filament material
Challenges of metal filament
- Highly brittle
- Highly fragile (Low weight can be supported)
- Abrasive (Due to metal powder tending to extrude)
5. ABS (Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) filament
ABS is a petroleum-based thermoplastic polymer filament that is the most commonly utilized filament along with PLA filament used for 3D printing. ABS is utilized in several sectors due to its durability, flexibility, strength, etc.
Benefits of ABS Filament
- Low-cost filament
- High flexibility, durability
- Various colors and blends are available
Challenges of ABS Filament
- Non-biodegradable
- Harmful fumes produced during printing
6. Wood filament
Wood filaments used for 3d printing are changing the face of traditional timber construction work. The 3D printed products designed and produced by using wooden filaments are aesthetic and can be designed as per an individual’s preferred wood and color tones. The wooden filaments are composed of 70% (PLA) + 30% wood elements.
Benefits of wood filament
- Easy to work with
- Aesthetic products can be achieved
- Can be 3D printed in affordable printers
Challenges of wood filament
- Flammable (High heat contact to be avoided)
- Difficult to print in small nozzle sizes (Minimum 0.5mm nozzles)
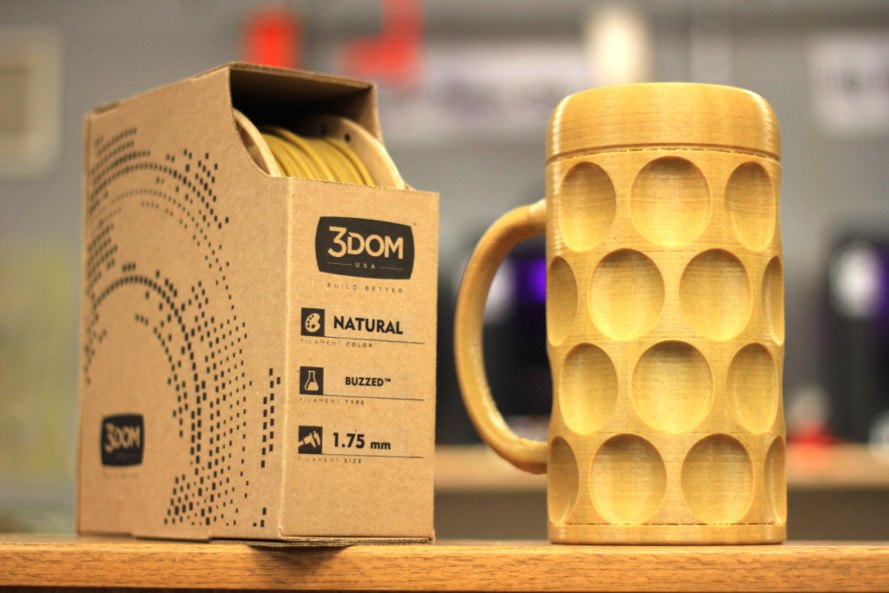
7. Waste by-product filament (Beer waste product)
Filament composed of beer waste products is an eco-friendly filament that is utilized for 3D printing especially consumer products. The composite filament is created using waste products from the beer brewing process mixed with a PLA base. The filament is researched, tested, and produced by several companies such as 3Dom, Veolia, Francofil, etc.
Benefits of Waste by-product (Beer waste) filament
- Aesthetic final products
- Sustainable filament option
- Reduce and reuse waste material by-products
- Easy to be produced using any PLA 3D printer types
Challenges of Waste by-product (Beer waste) filament
- The finesse to be achieved should be constantly observed during printing
8. Waste by-product filament (Coffee Ground)
A 3D printer filament made up of coffee grounds is an interesting approach to utilizing everyday waste products. It is a composite filament composed of coffee grounds fused with a PLA base. Some companies that are producing coffee ground filaments are 3Dom, Filament2Print, etc.
Benefits of Coffee ground filament
- Biodegradable
- Sustainable filament type
- Aesthetic products can be created
Challenges of Coffee ground filament
- Can string or ooze
9. Clay filament
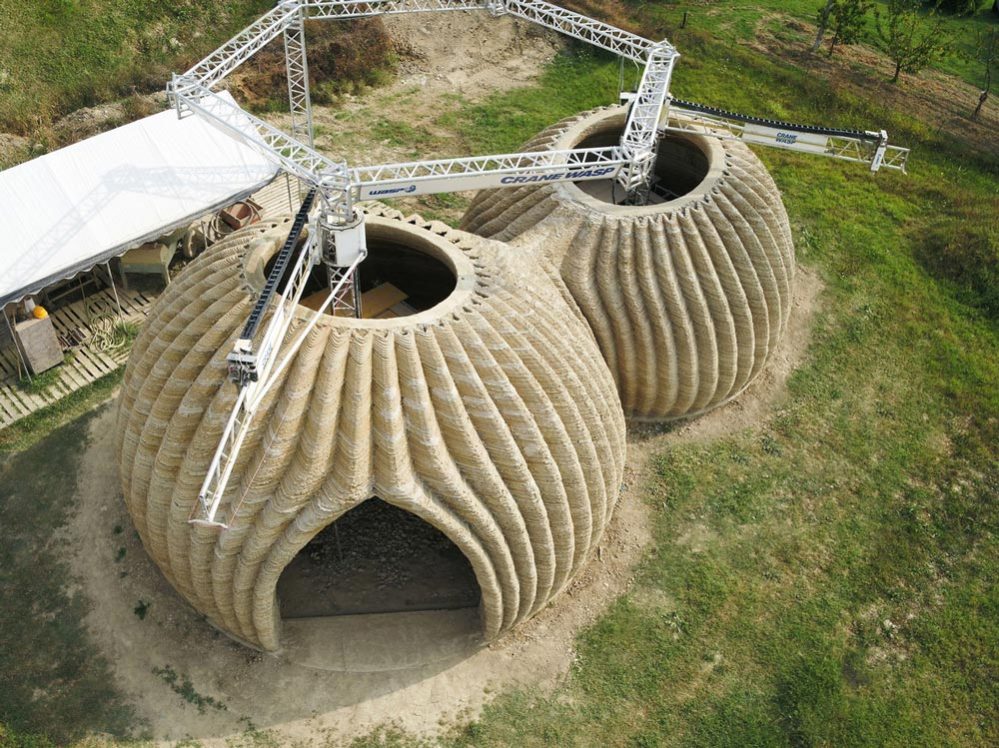
Clay filament utilized in 3D printing is a more sustainable printing option. The filament helps create products/structures that resemble real clay. This composite filament is extensively used in the construction and consumer sectors for architectural projects and consumer products.
Benefits of clay filament
- Durable
- Heat resistant
- Good printability and is easy to work with
Challenges of clay filament
- Good composite filament consistency to achieve the best products
10. Carbon Fibre filament
Carbon Fibre Filament is preferred for 3D printing due to its strength and light character. This composite filament is used to create high-quality carbon fibre products/structures in various sectors. It is integrated into standard filaments (PLA/ABS) or with nylon filaments, etc.
Benefits of Carbon Fibre Filament
- Lightweight
- Strong filament
- Heat resistant
Challenges of Carbon Fibre Filament
- Difficult to print using small nozzles
- Strong material nozzles to be utilized
11. Color-changing filament
The color-changing filament is a thermochromic filament that changes color with different temperatures. It is a composite filament type with a PLA base and color-changing property additive.
Benefits of Color-changing Filament
- Easy printing process
- Various colors are achieved at varied temperature
Challenges of Color-changing Filament
- Filament when printed when exposed to UV light/temperature becomes fragile
12. FPE filament
FPE (Flexible Poly ester) filament due to its soft and rigid properties is often suitable for demanding 3d printing sectors. The filament due to its strength and resistant properties has several applications ( sportswear, protective applications, etc).
Benefits of FPE Filament
- Light-weight filament
- Flexible and Durable
Challenges of FPE Filament
- Difficult to print and work with (Due to warping and poor adhesion)
13. Nylon filament
Nylon filament is a synthetic polymer known as thermoplastic which is extensively used for 3D printing from construction to consumer products sectors. Its characteristic flexible and impact-resistant property makes it a desirable filament material for flexible designs.
Benefits of Nylon Filament
- Strong and Durable
- Abrasion resistant
- Chemical resistance
Challenges of Nylon Filament
- High-temperature requirement during printing
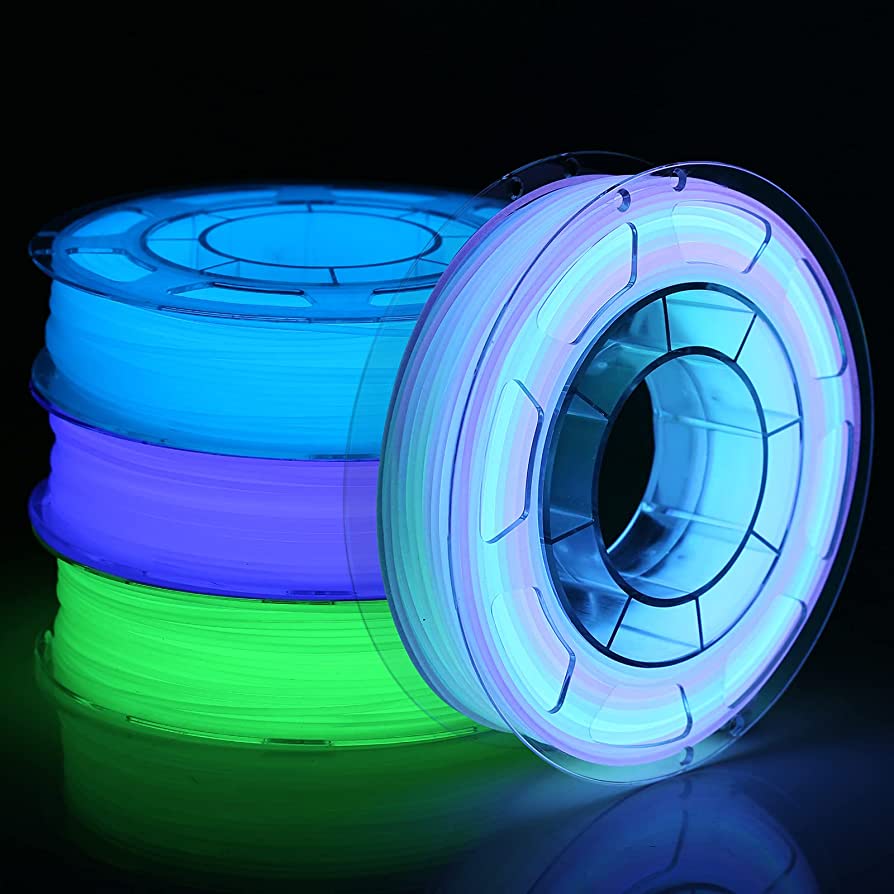
14. Glow-in-the-dark filament
Glow in the dark filament is another example of unique inventions in filament materials created in 3D printing. The additives added to the filaments help illuminate the filament in the dark. The UV light absorbing additives added are zinc sulfide /calcium sulfide, strontium illuminate, etc.
Benefits of glow-in-the-dark filament
- Various colored filaments can be created
- Glow-in-the-dark filament additives are abrasive
Challenges of glow-in-the-dark filament
- Glows only when charged under the light
- Glow varies with different additives added to the filament
15. HIPS filament
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) Filament is a copolymer composed of polystyrene and polybutadiene. The resulting filament is a copolymer that is sturdy and resilient compared to standard polymer filaments. It is used not only in the construction sector but also for consumer products (food processing, toys, etc).
Benefits of HIPS Filament
- Cost-effective
- A good supporter filament material
Challenges of HIPS Filament
- Warping (Constant heat is required to avoid warping)
- Not compatible as a support filament with all filament materials































Leave a comment