From science fiction dreams to scientific proposals, the prospect of life in space is no longer a distant dream. One question eclipses the rest as missions to Mars and the Moon are on the horizon: How will our homes exist beyond Earth? The production of intelligent, responsive materials is transforming the construction, design, and habitation of extraterrestrial dwellings since human beings are preparing to create a permanent habitat on the Moon, Mars, and elsewhere.
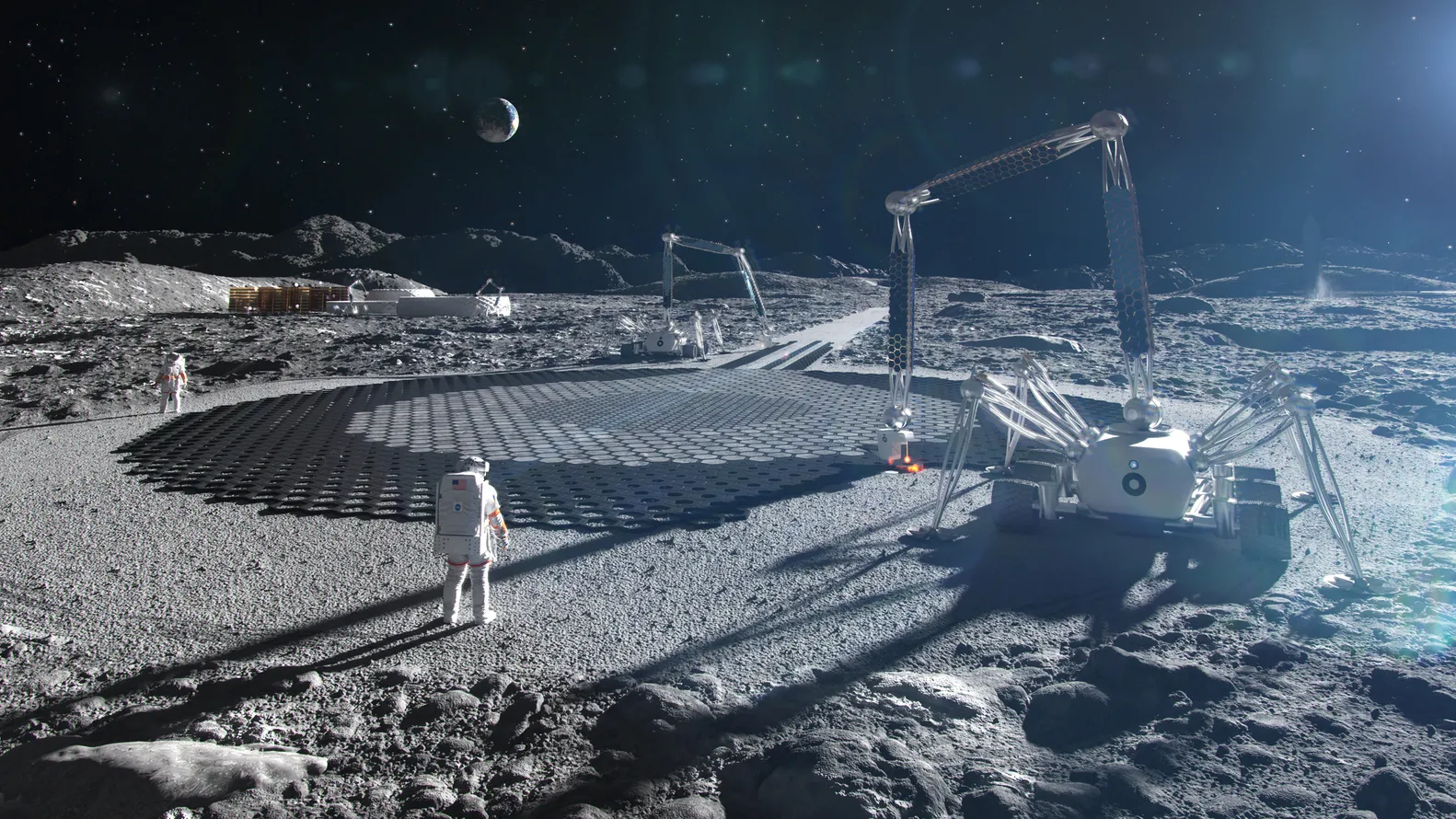

What are Smart Materials?
Smart Materials are designed to react to the environment in a specific manner. They alter shape, colour, or strength as a response to stimuli including temperature, pressure, light, or radiation. These technologies, from self-healing plastics that repair cracks on their own to shape-memory alloys that flex and straighten back up, are necessary in order to endure space’s unforgiving environment.
Launching objects into space is expensive. Nanolattices and inflatable modules are available. Soft, lightweight structures can be compressed to be launched and then inflated in space, says NASA’s Bigelow Expandable Activity Module.
The modules are extremely tough without being bulky, as they are radiation-hardened polymers and intelligent textiles. In the meantime, structures with the least amount of mass and the greatest amount of strength can be constructed with the aid of nanolattices, which are extremely strong and light.
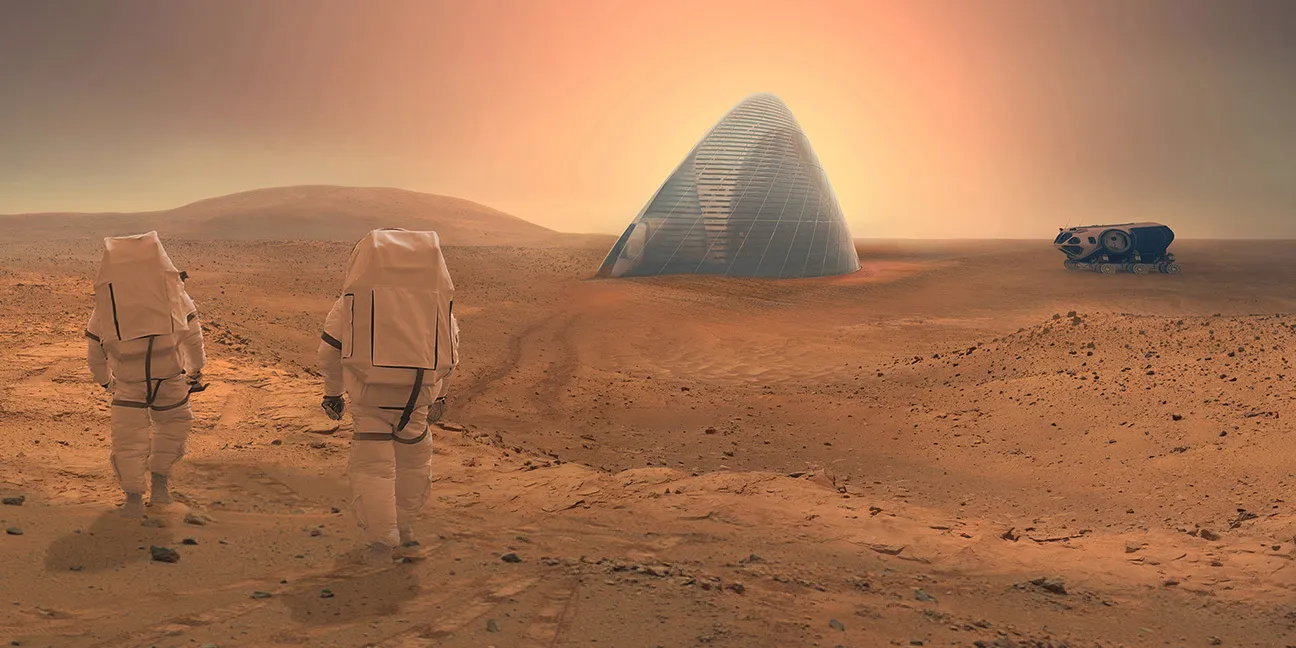
Buildings that Adapt and Transform
Static housing can be changed into dynamic, living spaces through the use of smart materials. Shape memory alloys are ideal for morphing structural components such as habitat doors that can shut themselves up or insulation panels that can change because they alter their structure with changes in temperature. Like sunglasses for your Martian home, thermochromic and electrochromic coatings change colour to manage light and heat.
Space radiation is a deadly hazard. Traditional shielding must be dense and bulky. Intelligent solutions, such as building blocks composed of mycelium, offer a light, naturally insulating material that forms on site. Self-healing polymers, on the other hand, provide structure without demanding human intervention by sealing microcracks independently from radiation or micrometeoroid strikes.
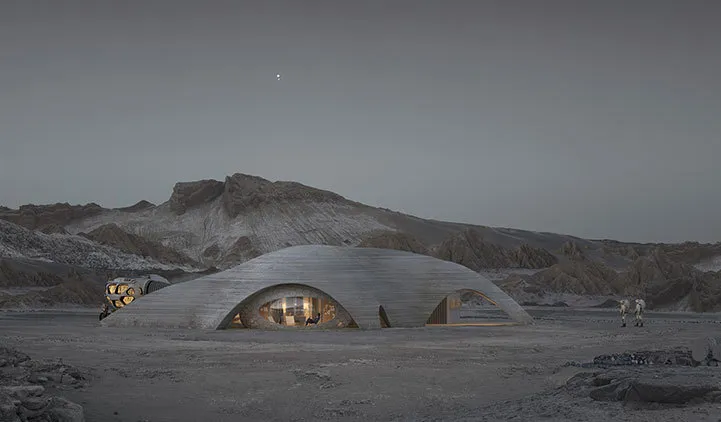

Building With What Already Exists
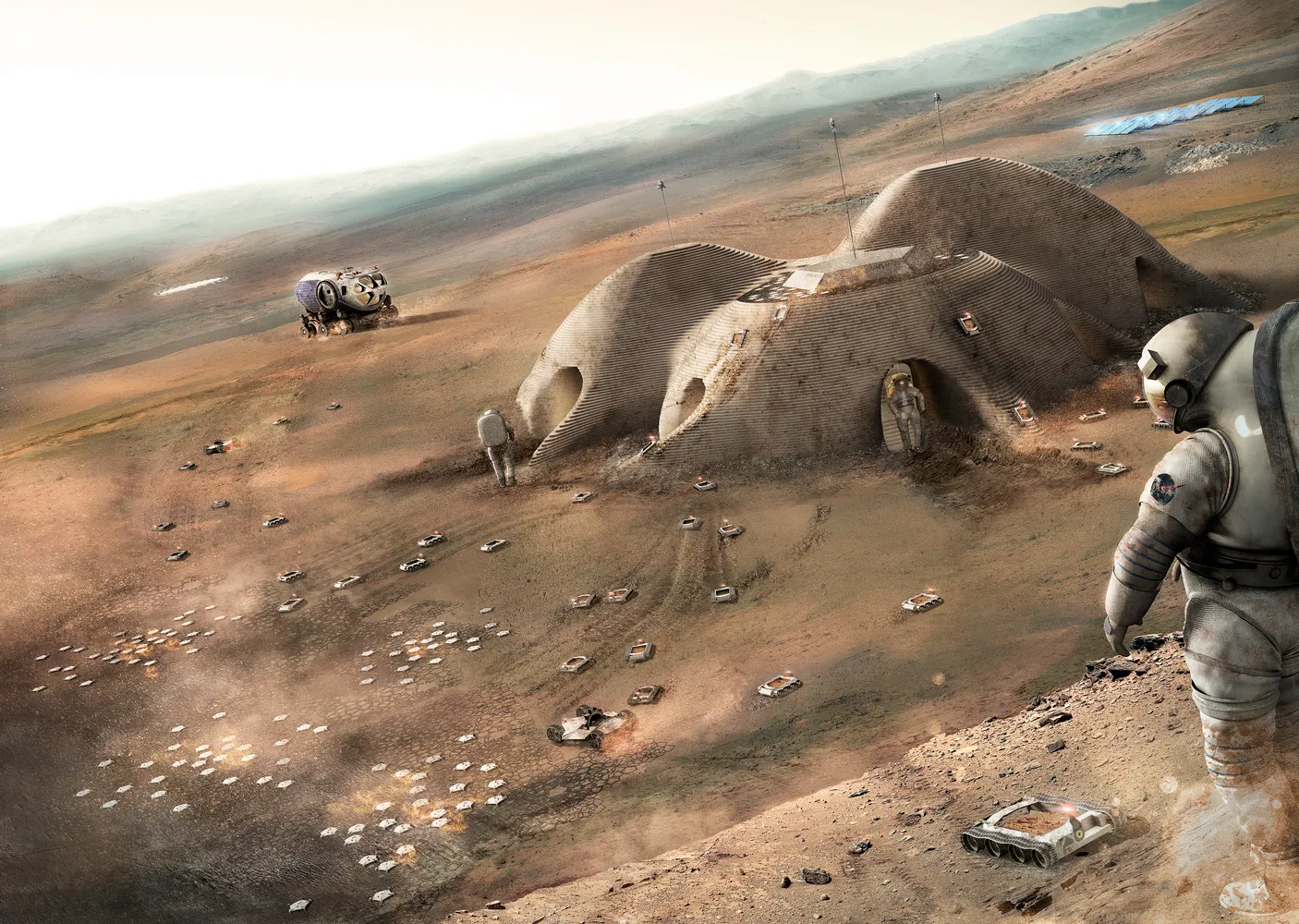
3D printing with Martian regolith rather than shipping raw material is possible. Smart materials are at the heart of in-situ resource utilization. Regolith can be reshaped by AI-powered robots and smart binders into insulating, long-lasting structures. ICON and programs like NASA’s MMPACT are already exploring these processes, which are pushing the envelope for autonomous extraterrestrial construction.
Materials that harden in hostile environments and structurally change over time can be engineered by combining them with smart geopolymers or proteins within a very short time frame. During curing, certain materials even heal themselves to become stronger by reacting to local pressure and temperature. Using Martian dust alone and a smart printer could construct cities on Mars.
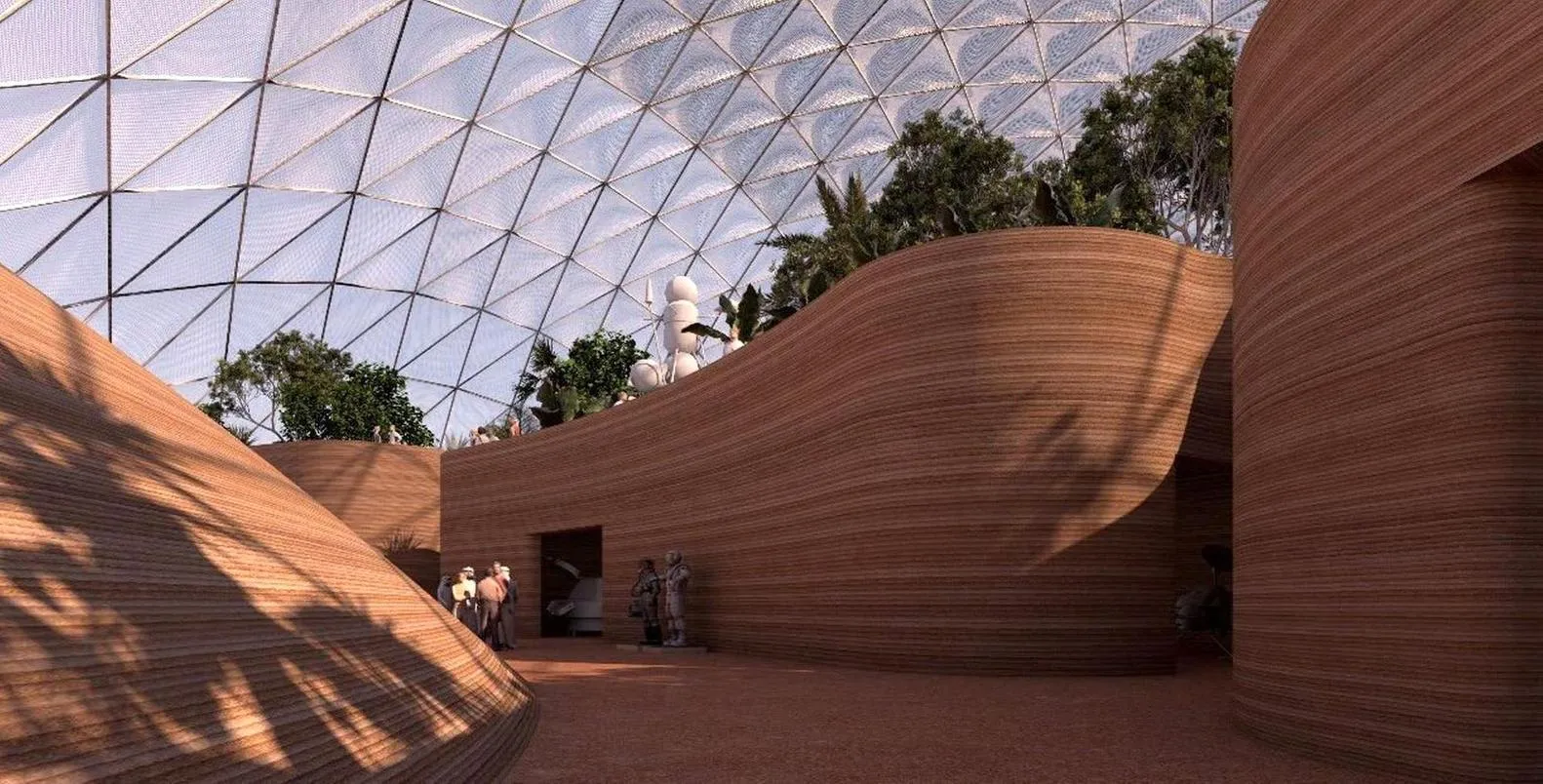

Smart Skins for Climate Control
Despite environmental extremes, space habitats should also achieve stable internal temperatures. Dynamic heat flow control is achieved through variable thermal emissivity smart skins. By their capability to alter their thermal characteristics in response to the environment, such materials minimize mechanical heating and cooling. Consider a habitat that insulates at night and cools itself on a Martian day.
Solar skins which generate electricity and give heat to the people inside will be part of homes in outer space in the future. Thin-film solar cells and nanocoatings can be used to engineer these materials to adjust how much power they draw when light hits them.
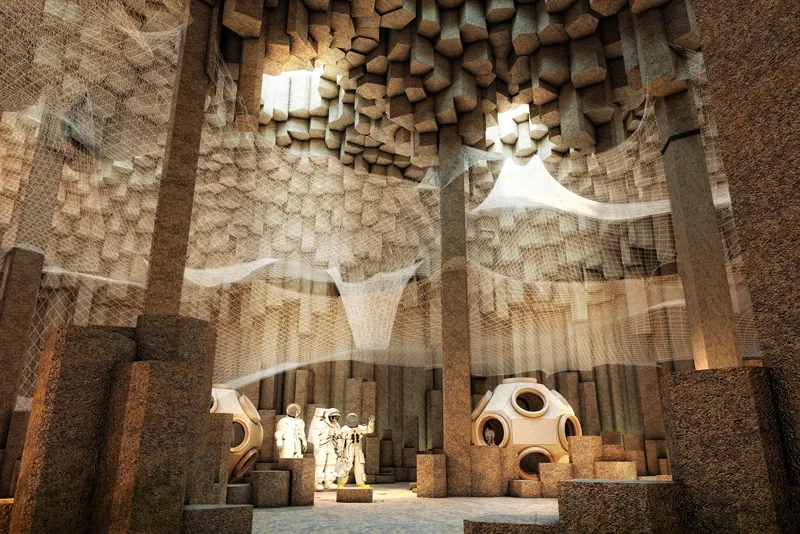

Looking to explore space architecture? Check out “Mars Architecture – Studio Valentina Sumini” to learn more about computational design capabilities of design that can be applied to space architecture.
The Impact of Technology
All surfaces count in space. With the addition of flexible photovoltaics to external habitat walls, roofs can be turned into sources of energy. Such smart energy-harvesting skins provide thermal shielding along with powering life support systems. The concept makes habitats self-sustaining ecosystems through the integration of architecture and function.
With AI, smart materials are even more powerful. Autonomous habitats that sense anomalies and automatically repair themselves are being created by NASA’s Space Technology Research Institutes, like HOME and RETHi. Imagine a living module that, without human intervention, senses structural fatigue and changes shape based on it.
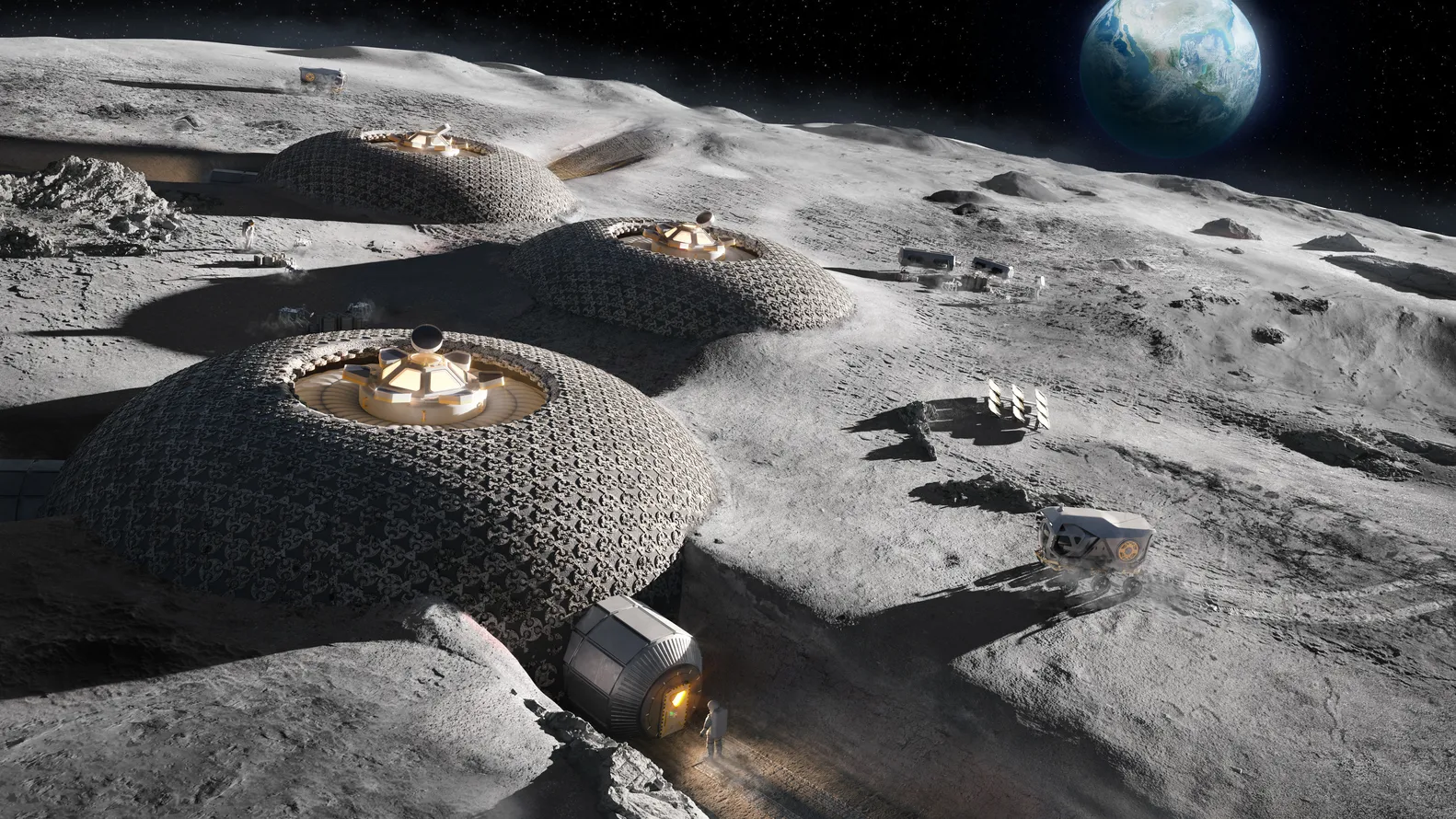

Designed for Human Wellness
The aim of living in space is not merely survival. Intelligent materials serve physical and mental well-being too. Shape-memory composites create reconfigurable interiors that allow personal space and diversity, and adaptive lighting schemes mimic the day-night patterns of the Earth. There are even systems that integrate smart lighting with hydroponic farming to deliver fresh food to tiny, climate-controlled environments.
Innovations from Space architecture are making their way back to the world. Green building design is evolving through energy-efficient skins, adaptive building envelopes, and self-healing concrete. Inflatable, self-deploying structures, once envisioned for space, may soon serve as emergency shelters. Smart materials are bridging the gap between resilient habitats on Earth and extreme environments in space.
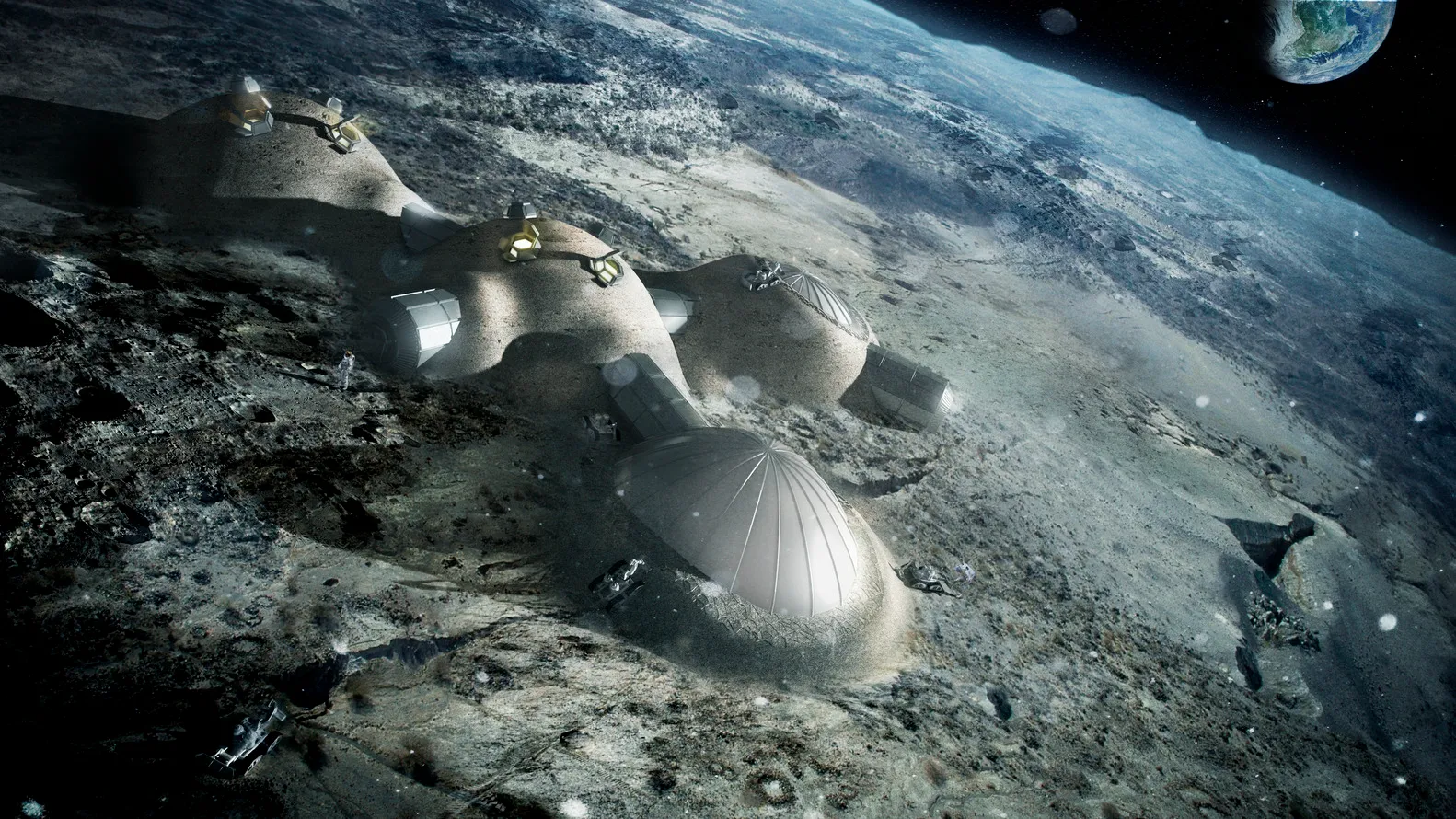

What the Future Holds for Space Habitats
While the potential of emerging technologies is undeniably exciting, it’s important to acknowledge the real-world challenges that must be addressed before they can be widely adopted. Continuous testing is essential to ensure these systems perform reliably, especially in harsh or unpredictable environments.
We want smart, capable systems, but with increased complexity comes a greater risk of failure. And beyond functionality, we must also consider the environmental impact and ethical implications of deploying these innovations on a global scale.
Smart materials are quickly becoming the building blocks of next-generation off-world homes, this is no longer science fiction. They deliver robust, efficient, and context-sensitive architecture, from lightweight, flexible skins to radiation shielding and even self-healing capabilities.
Intelligent materials will allow us to build homes off Earth as we embark on the space age, homes that will survive, adapt, and nurture human life in the most extreme conditions. Materials that can think, sense, and heal are essential to the future of space habitats, engineers, architects, and visionaries.























Leave a comment