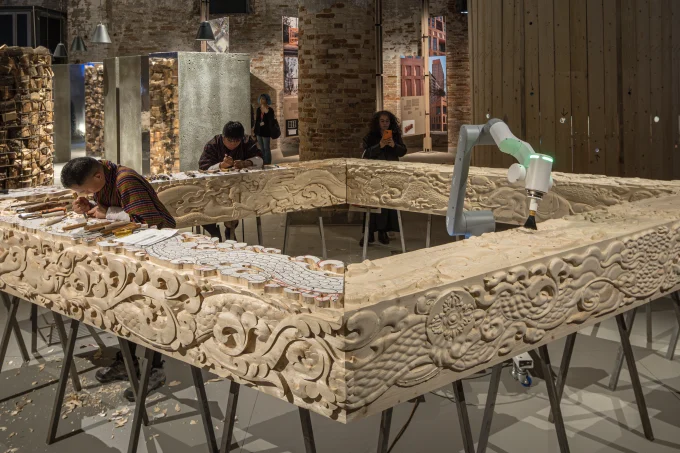
Robotics has always inspired a keen sense of curiosity and interest among individuals. Precision and accuracy are prime factors that one strives for in work production, and achieved by robots are curious to everyone. Robotics has been utilized now in several sectors of society. The architecture and construction sector utilizes robotics in designing and producing precise designs and products. Robotics in Architecture is an evolving technology implementing robotics for accurate models and structures.
Robots and the Future
In the future, robotics and technology utilization in building architecture and construction will be an important part of the construction sector. Intricate designs and structures are now convenient to construct with robot applications during the design and construction phase. Architects are utilizing robotics in architecture to help create efficient forms and structures.
Benefits of using robots in architecture
Robot application in architecture and the construction sector poses several advantages and benefits in comparison to human workers. Complex and precise designs and construction seemed impossible in the past, but not anymore with robot applications. Some of the benefits of robot utilization in architecture and construction;
- Precision and Quality – Robots can create precise and accurate structures, especially with respect to their form and structure. The accuracy and precision brought by robots can help create designs and products of better quality. Robots utilized in designs create architecture with minimal issues or inconsistencies. Products and structures designed are consistent in terms of their shape, form, and quality.
- Long work span – Humans are prone to distractions, stamina, and attention; hence, the working span is reduced compared to robots. Robots can complete the given task for an entire day through the entire week, whereas human work is time-bound and restricted. Robots can help reduce the time required for construction due to the long work span achieved by robots.
- Speedy construction – Robots make a man’s life easier for every individual, especially in the construction sector. The time taken to build a structure by a robot is less in comparison to manual labor. The time taken is shorter but also the structures designed are more efficient.
- Avoids Mishaps – The probability of errors occurring is less; hence, the mishaps or accidents prone to occur are also less. Accidents that are prone to occur through manual labor are reduced and avoided considerably by robots.
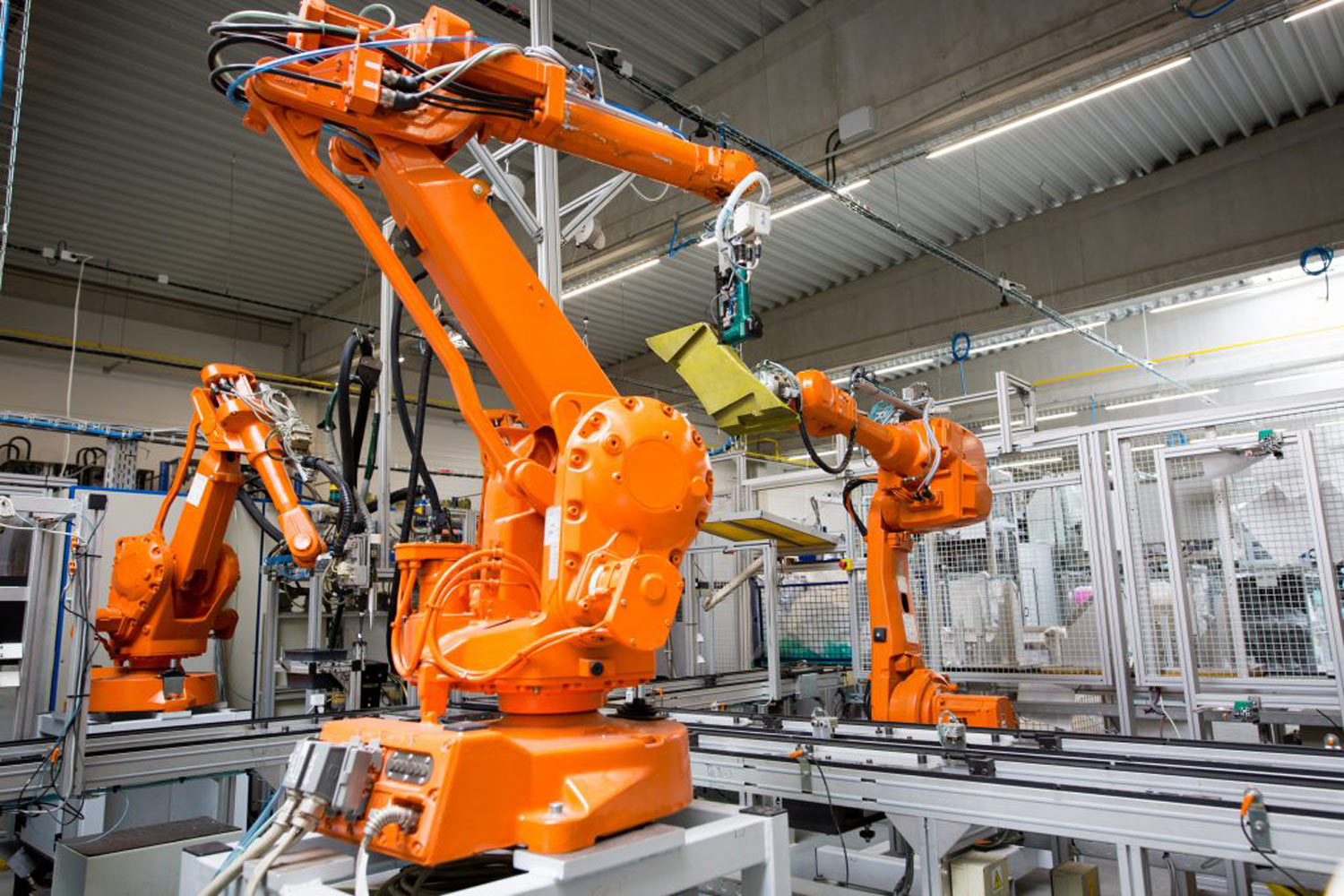
- Several tasks can be achieved – Several difficult tasks can be carried out by robots compared to humans. Dangerous tasks can be carried out without the concern of mishaps or injuries that could occur by manual labor.
Applications of Robots in Architecture
Robots and automation have been integrated with architecture and construction to help carry out several tasks. Some of the applications of robots in architecture are;
- Creating models and structures of various scales – Architectural 3D models can be created using robots with precision and accuracy. Complex and intricate architecture can be built using robots that showcase precision. Small 3D models to large-scale live structures are possible now with robot utilization.
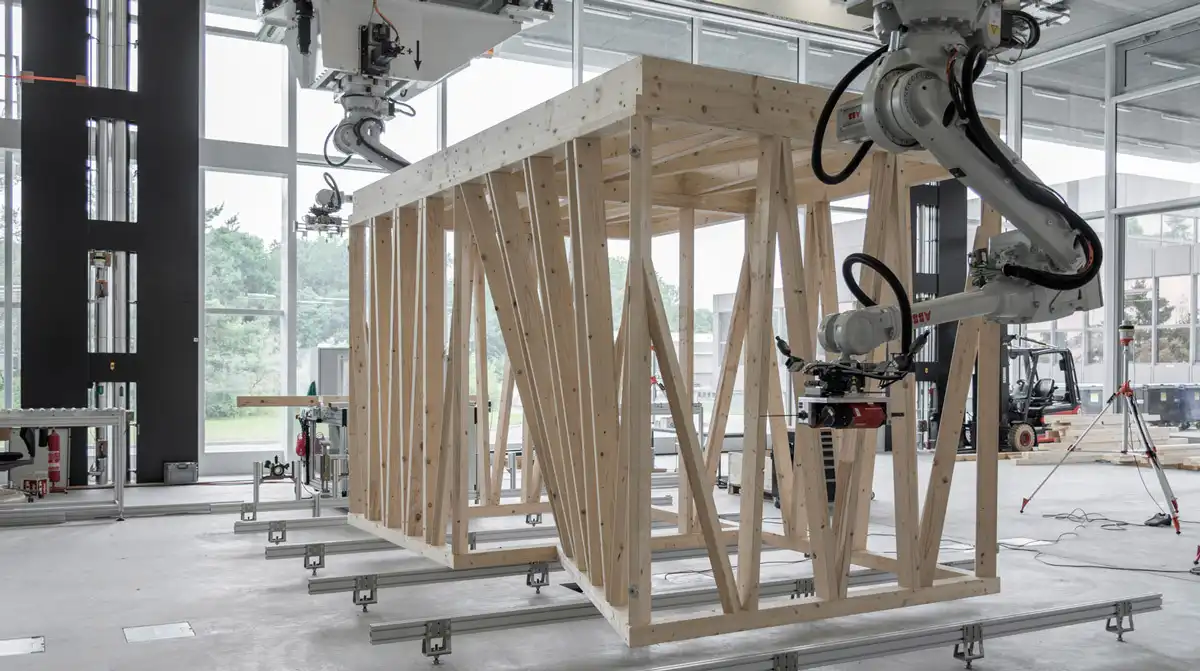
- Building construction elements – Robots can build buildings and construction parts accurately without any errors. Several building parts could be built beforehand which makes the construction process convenient. The entire process can be done by the robot in a lesser amount of time.
- On-site structure assembly—Construction on-site is even faster with robots. Machines can now easily assemble fabricated structural elements. Robotic engineers are implanting long robot arms in construction sites to lay bricks, arrange structural elements, and more.
- Robotics and structural integration—Buildings are now integrated with machines and robotics for indoor regulation. Automated robotics and machines can now regulate temperature, heat, and indoor air quality.
Listed here are ten structures, materials, and installations built by robots that are transforming architecture and construction sectors.
1. Flight Assembled Architecture
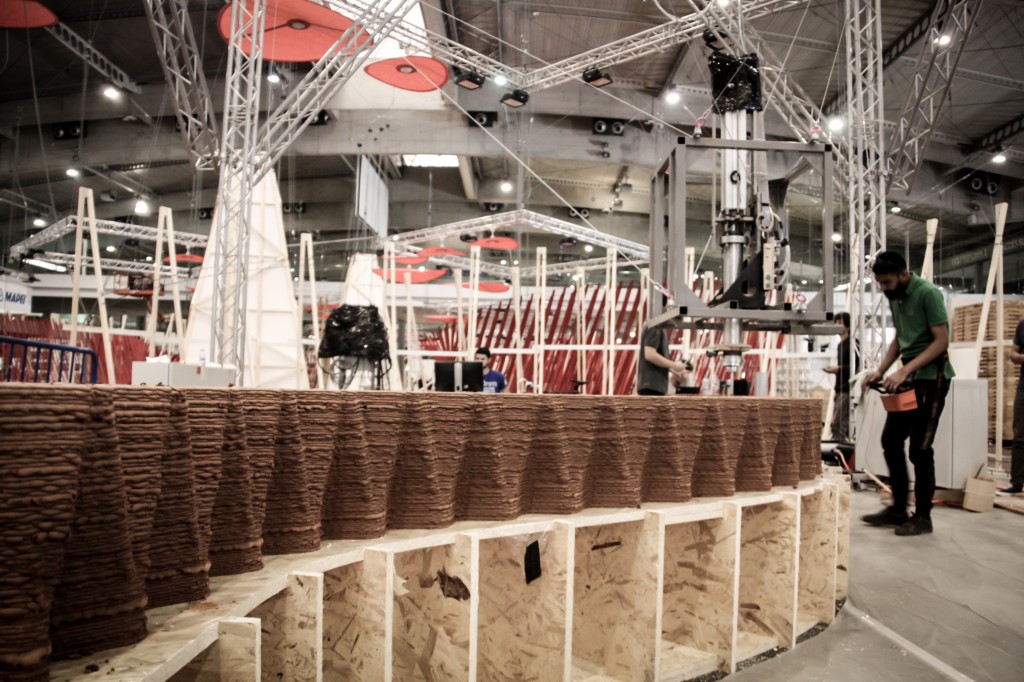
Flight assembled architecture created by Swiss Architects Fabio Gramazio and Matthias Kohler with Raffaelo d’Andrea (Roboticist). Flight-assembled architecture is an example of how different types of robots can be integrated in the architecture and construction of structures. Flying robots assembled a six-meter-high tower installation at the FRAC center in France (2012). The tower was composed of polystyrene bricks light in weight for drones to lift, with 1,500 elements stacked. The installation was an example of how robots can be utilized for creating complex yet accurate building-scale structures.
2. DFAB House – NCCR Digital Fabrication
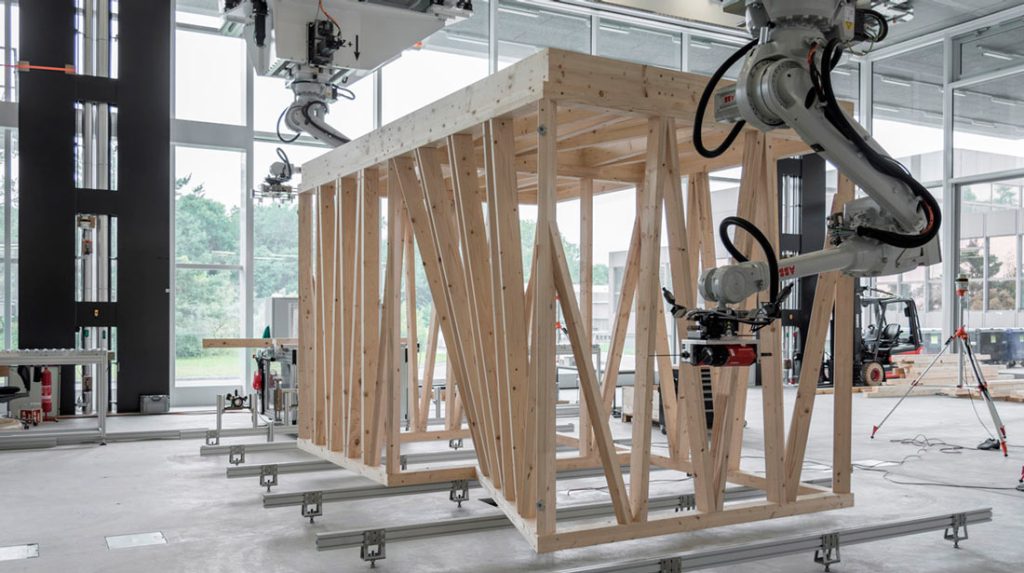
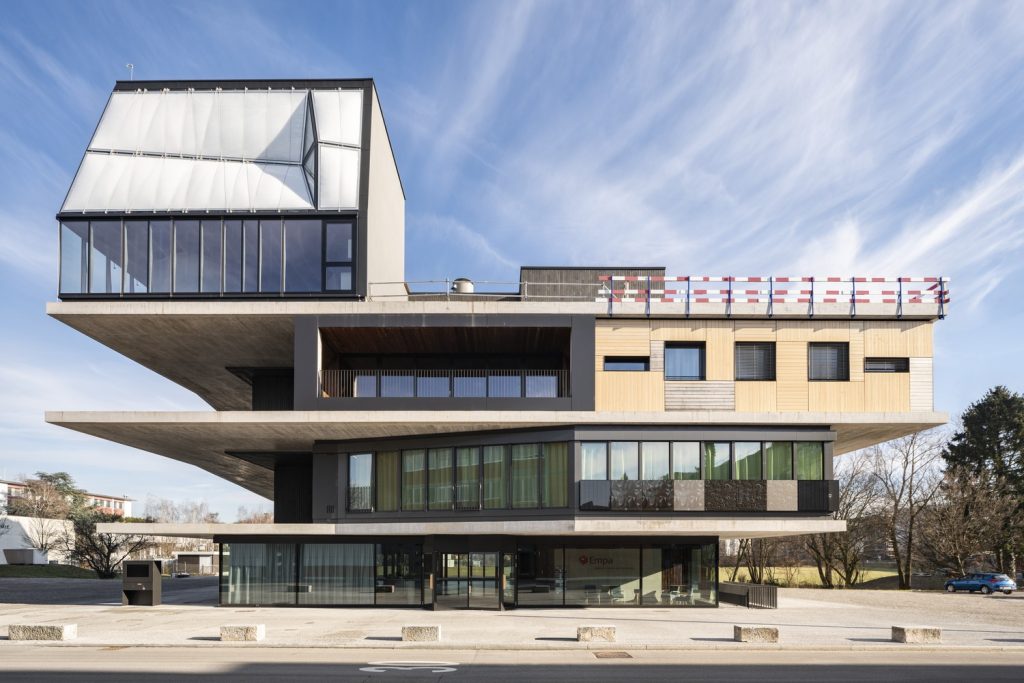
The DFAB House is a futuristic structure that has utilized robots in every stage of the construction process. The house is the first live-scale structure built using robots and modern fabrication methods. The project was an initiative by the NCCR Digital Fabrication, aiming to create a structure that showcases technological advancement in architecture. The project utilizes 3D printing and robotic fabrication technology and has used six research innovations. Prefabricated structural elements have been created by robotic technology and assembled on-site by robot application.
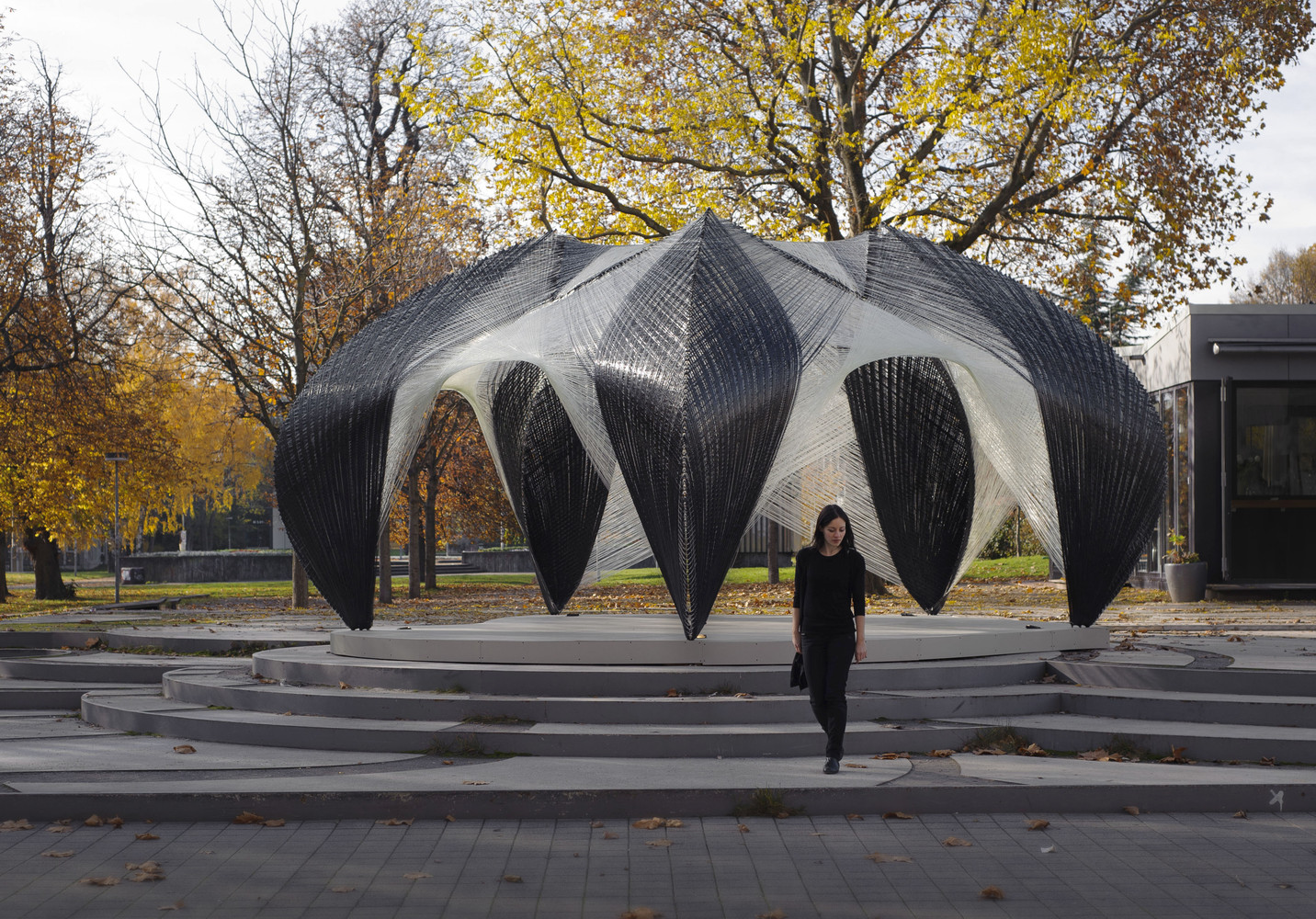
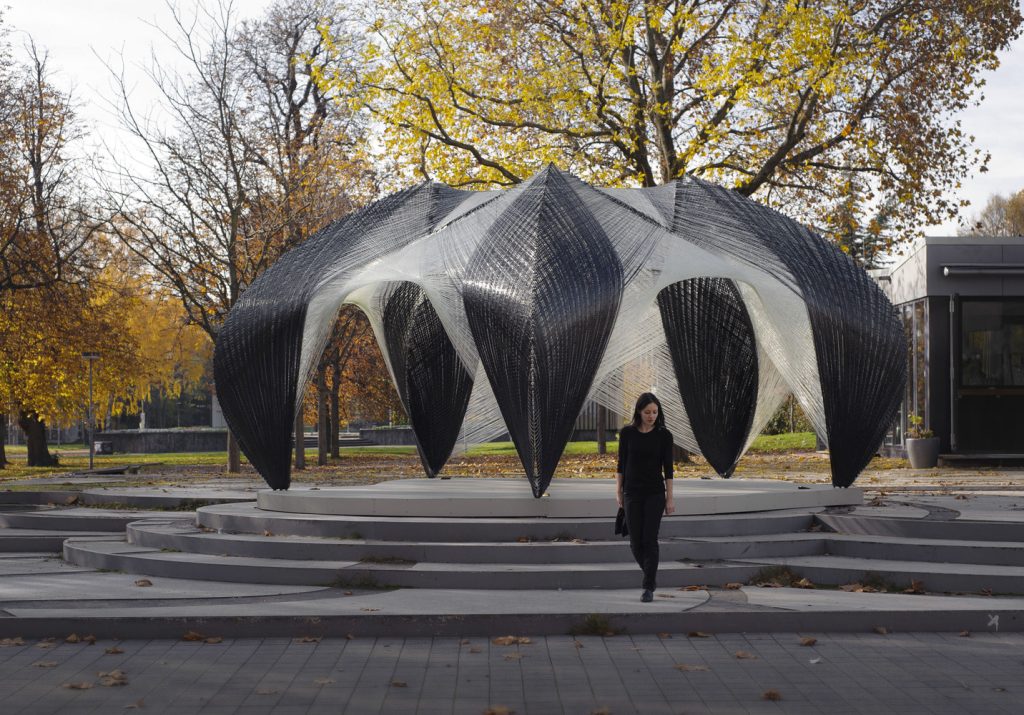
3. ICD-ITKE Pavilion / University of Stuttgart
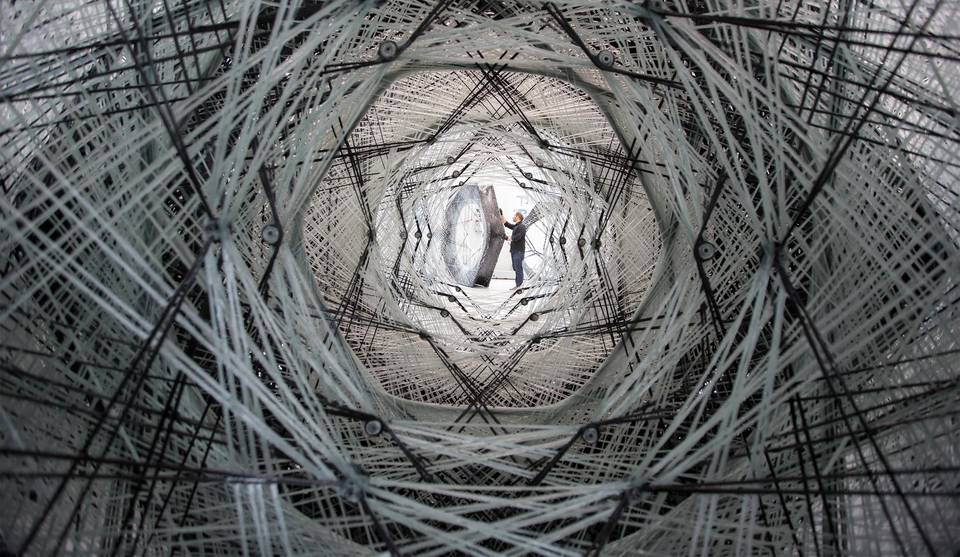
The research pavilion was designed by the Institute of Computational Design (ICD) and the Institute of Building Structures and Structural Design at the University of Stuttgart (2012). The composite (carbon and glass fiber) pavilion experiments on the fabrication and construction process. The project explores and focuses on exoskeleton and creating composite structures based on these principles. The fabrication process was performed utilizing a six-axis robot with an external seventh axis. The fibers are spun on a temporary frame in a circular motion by robots.
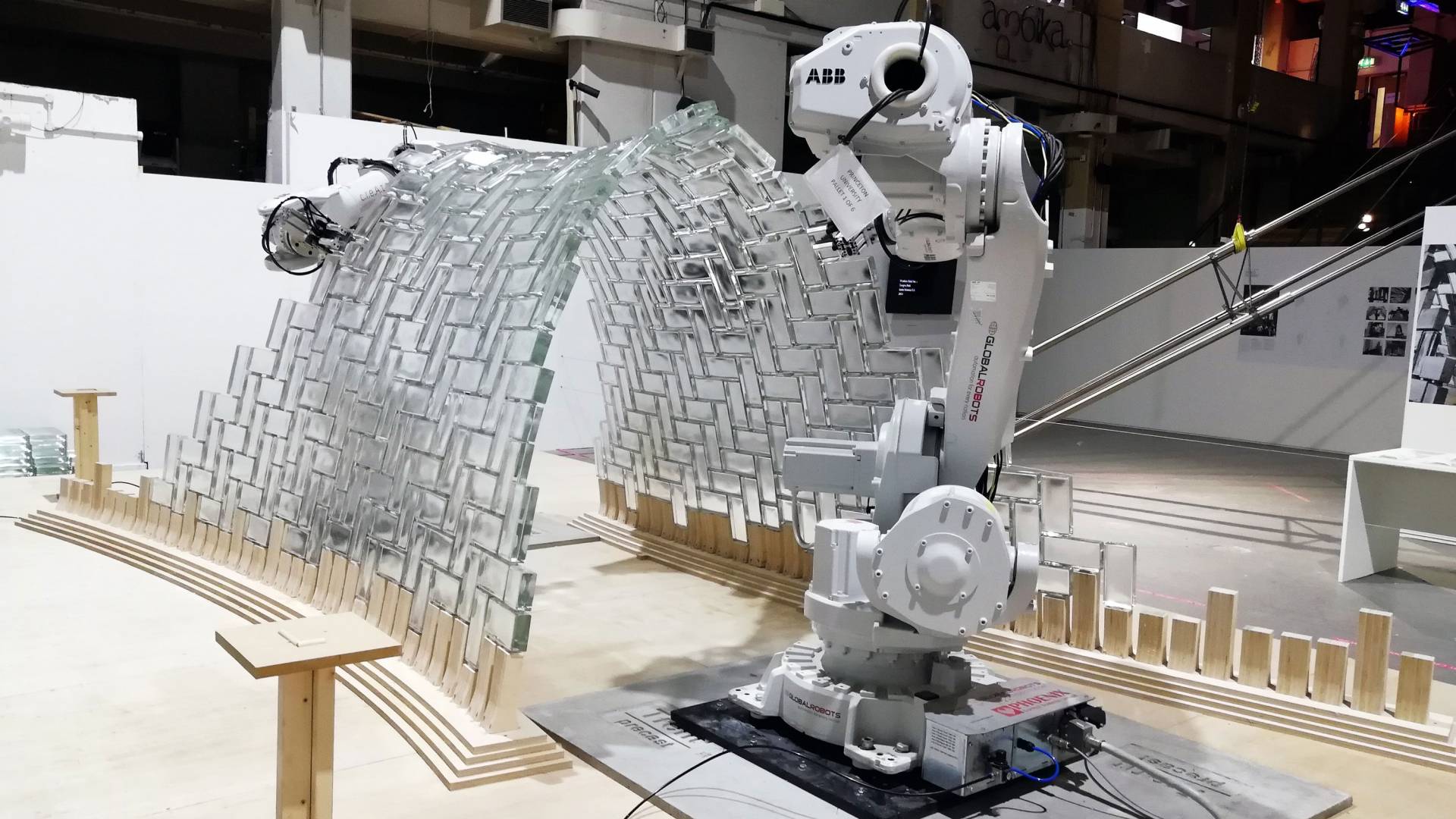
4. SOM Exhibition – Anatomy of Structures
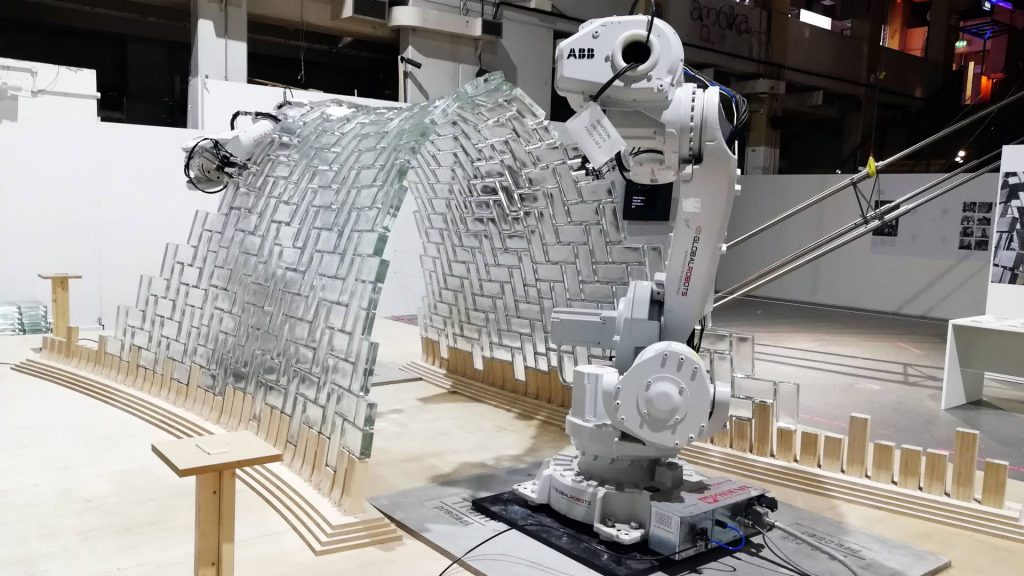
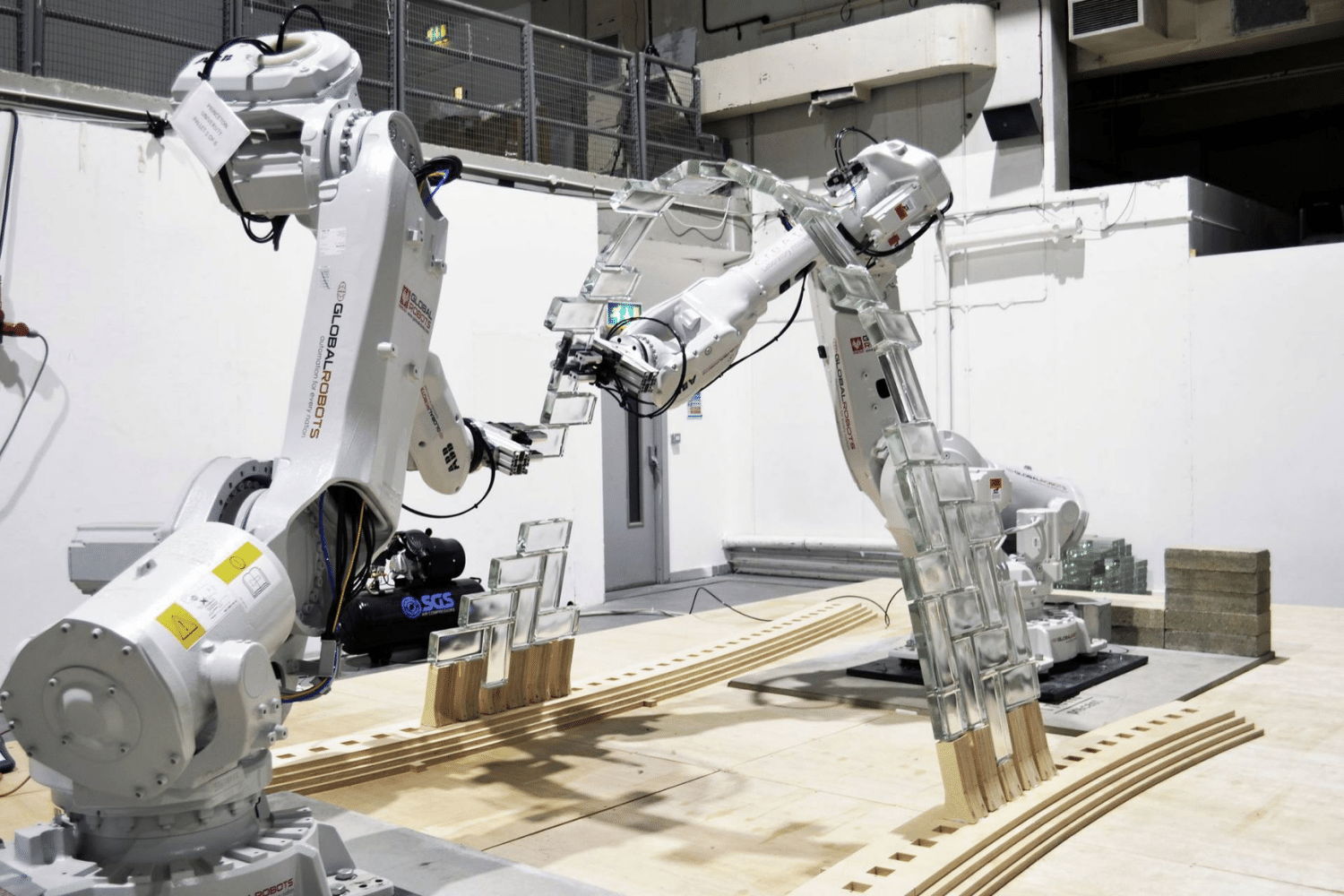
Complex forms and structures require precision and accuracy now they can be easily accomplished utilizing robots. Two Princeton researchers, Stefana Parascho (Architect) and Sigrid Adriaenssens (Engineer) collaborated with the renowned architectural firm SOM. They created a unique installation for the SOM Exhibition (Anatomy of Structures) in London. The installation used industrial robots to create an astounding vault consisting of glass bricks. It is 2.1 metres tall and is composed of 338 transparent glass bricks. The structure referred to as the Light vault is efficient, and reduces the number of materials required for the construction process.
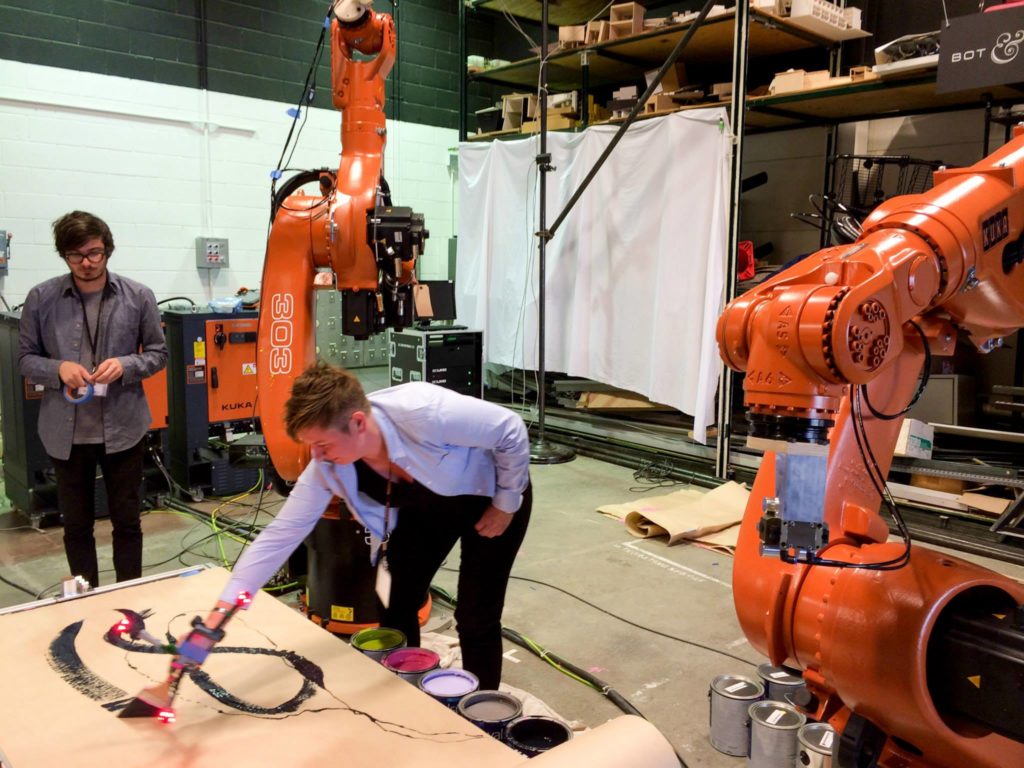
5. ROB/Arch 2012, Vienna
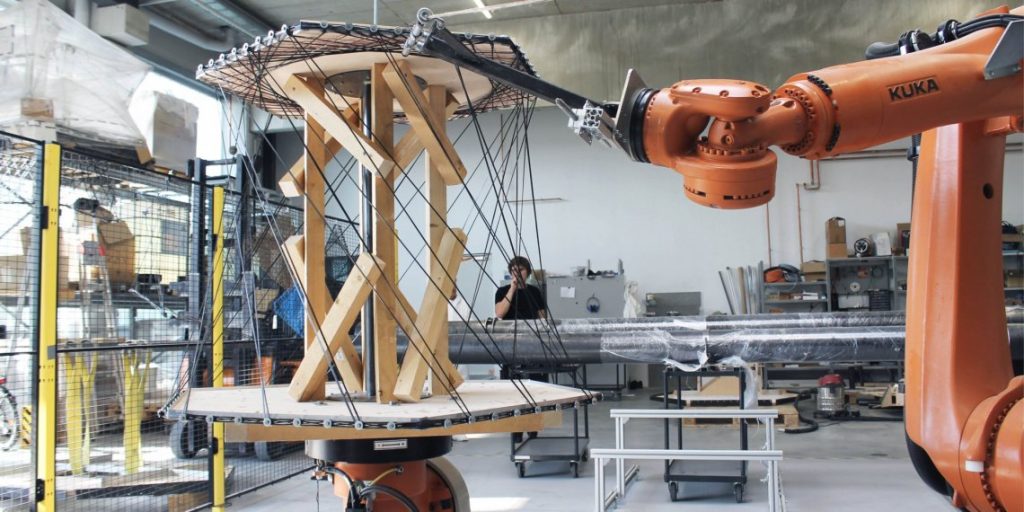
The ROB/Arch conference was held in Vienna (2012) and showcased Robotics in Architecture. The conference presents a platform that helps showcase innovative applications of robots in the creative industry. Individuals from various creative fields, artists, architects, and designers explore robotics. A robotic arm was developed by Harvard to create clay material used for construction. Raw materials are integrated with robots and software to create construction materials. Fabrication of structures utilizing robots with digital software programs.
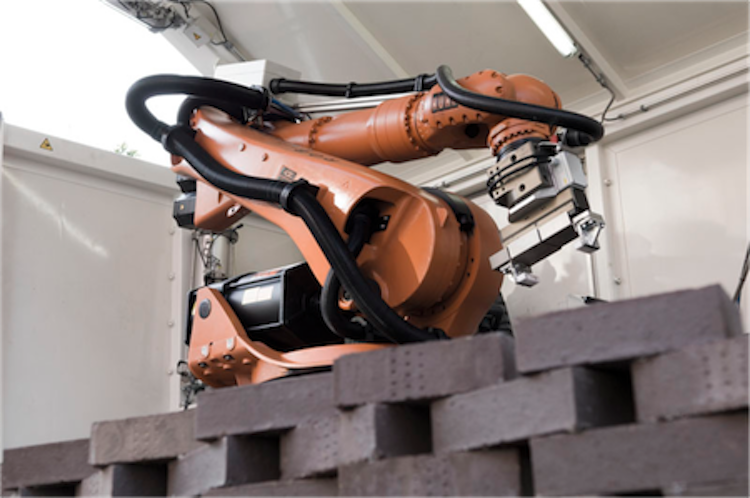
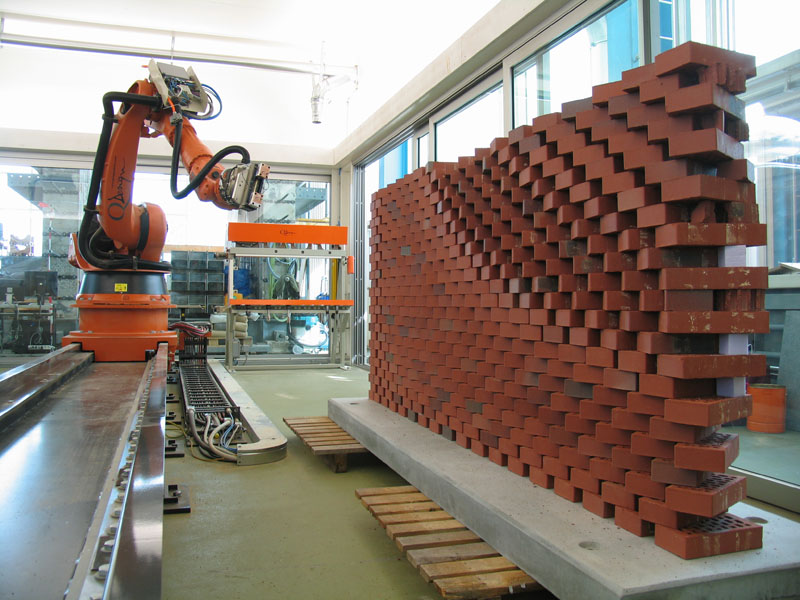
6. The Programmed wall – ETH Zurich
The Programmed wall is a designed brick wall that utilizes an industrial robotic arm for the building process. The conventional construction material brick is now evolving with technology and robots, even the laying and construction process. The robot arm is utilized to lay brick that has been taught at ETH Zurich by the Swiss architects Fabio Gramazio and Matthias Kohler. A brick wall with over 400 bricks was laid by the robotic arm in a twisted profile form. The arm was controlled by an algorithmic design tool that can easily command the arm.
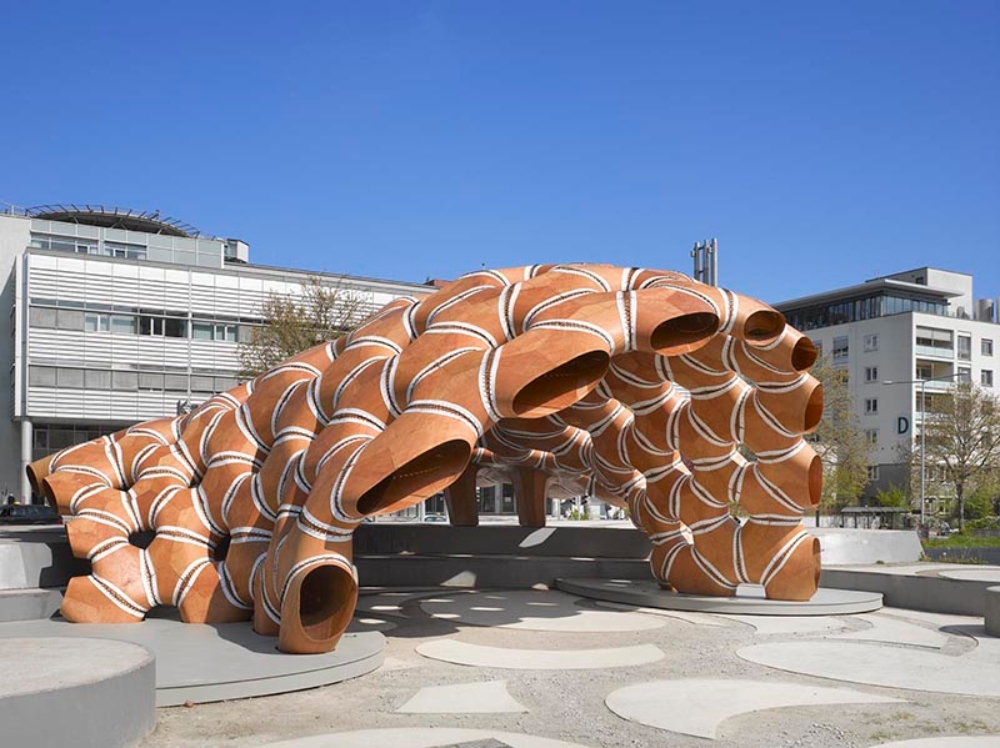
7. ICD-ITKE Pavilion – 2015-16
The research pavilion was designed and built by the Institute of Computational Design (ICD) and the Institute of Building Structures and Structural Design. The research partners have created a timber shell pavilion inspired by the sea urchin. The project experiments and utilizes robotics for stitching and creating the organic pavilion. An industrial robot is utilized in the assembly and bending process of plywood strips to form a segment and element of the pavilion shell. The project breaks the boundary between the material and the technological application.
8. The Stacked (West Fest) Pavilion
Complex timber structures that require precision and accurate construction are convenient now by utilizing robots. This pavilion was a temporary spatial structure for a public event at Canton Zurich. The wooden structure designed by Fabio Gramazio and Matthias Kohler has implemented robots for the fabrication process. The entire wooden structure is composed of 372 slats cut and assembled by robots. The robots utilized are controlled by algorithmic patterns. The project is an example of architecture that displays robotic application that transforms traditional construction materials.
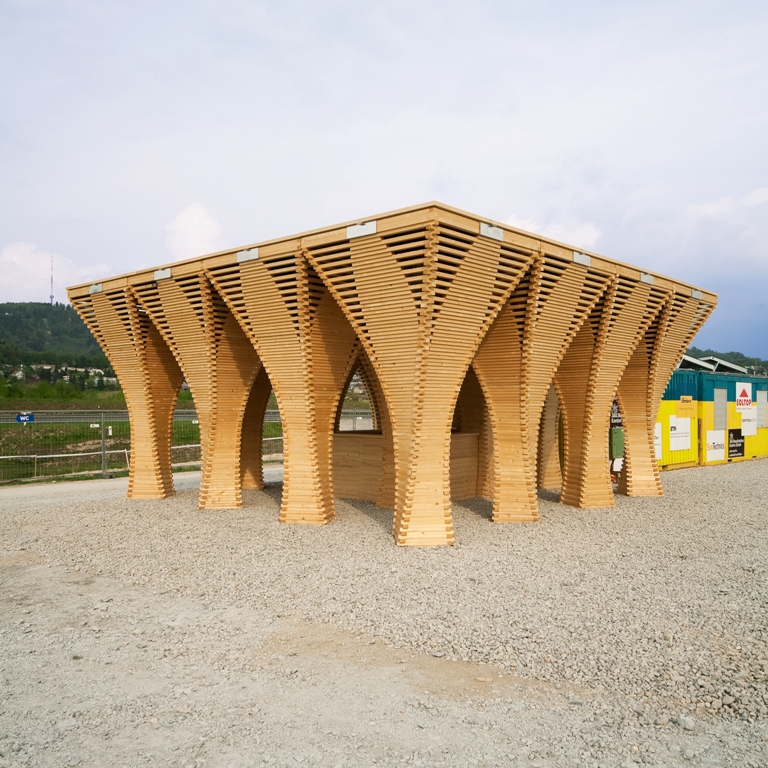
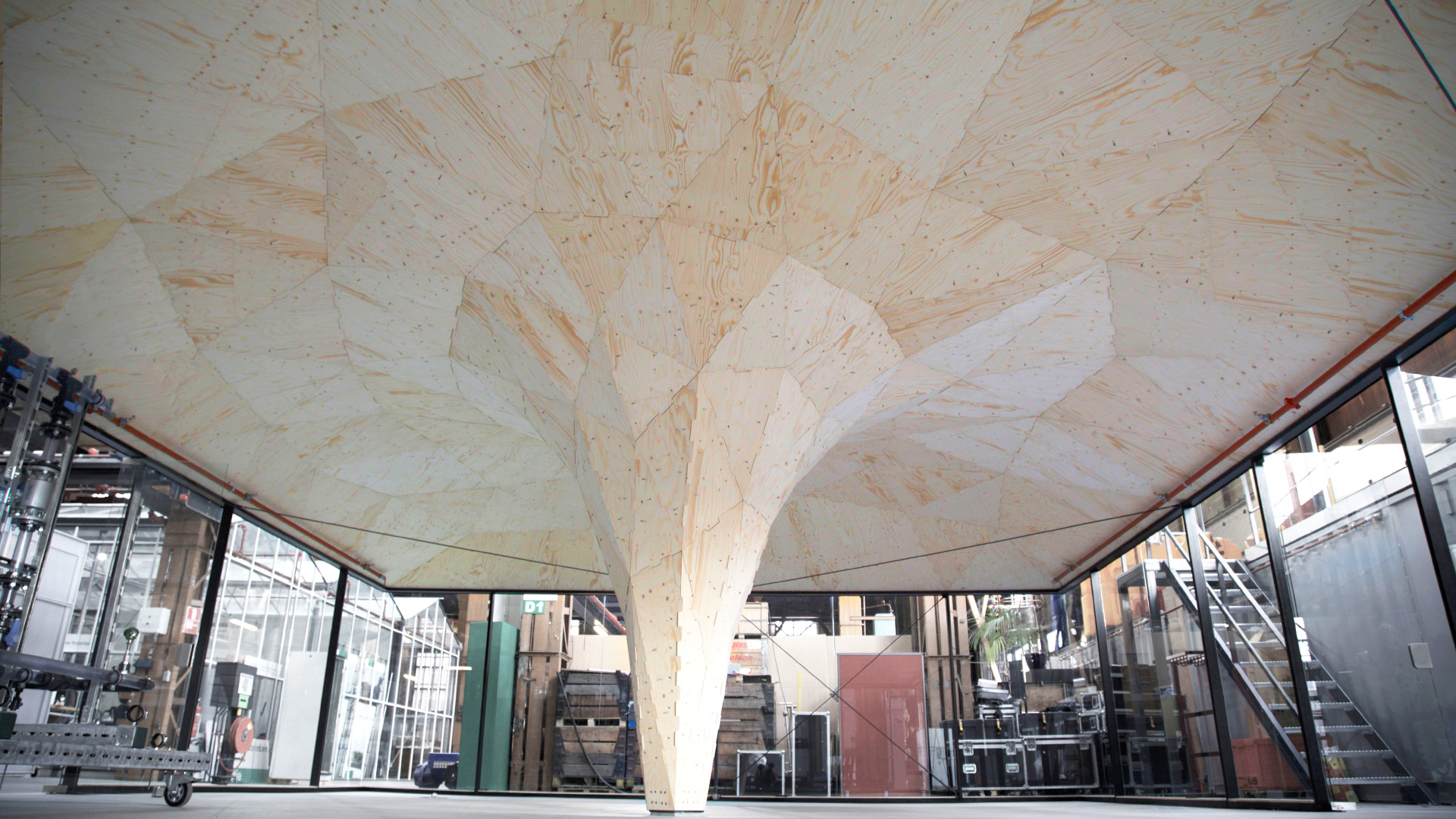
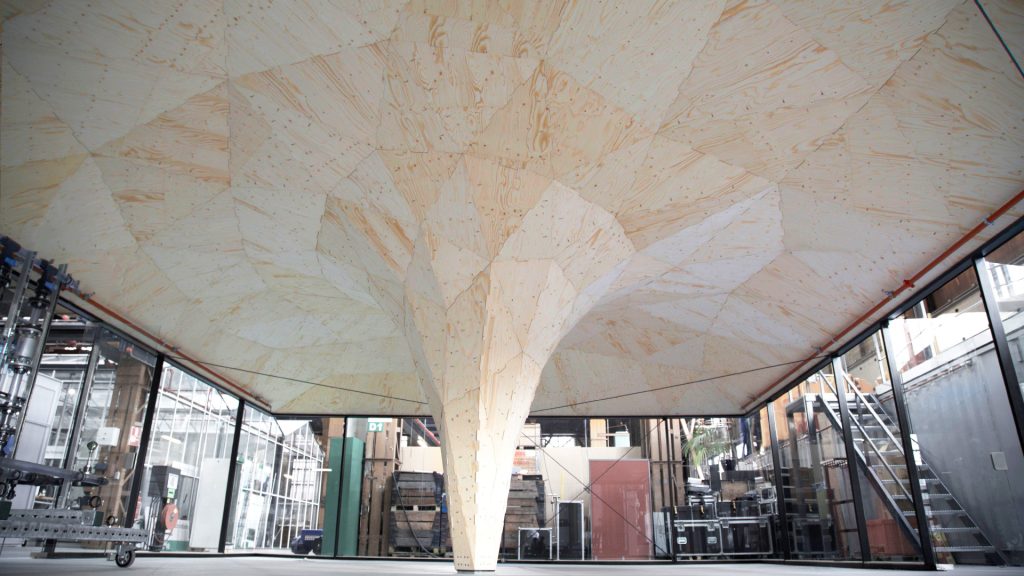
9. Skilledln Office Pavilion
The Skilledln Office Pavilion, designed by Studio RAP, is the first robotically fabricated structure in the Netherlands. It is located in Rotterdam’s Innovation Dock, an education and technology center. The entire structure was designed utilizing a robotic arm in integration with Rhino digital software. Wood is the primary construction material utilized in constructing the pavilion. The pavilion is composed of 225 wooden pieces assembled to create a vault of 8m wide roof pavilion. The smooth vault rises from a central column, which blends into the roof structure.
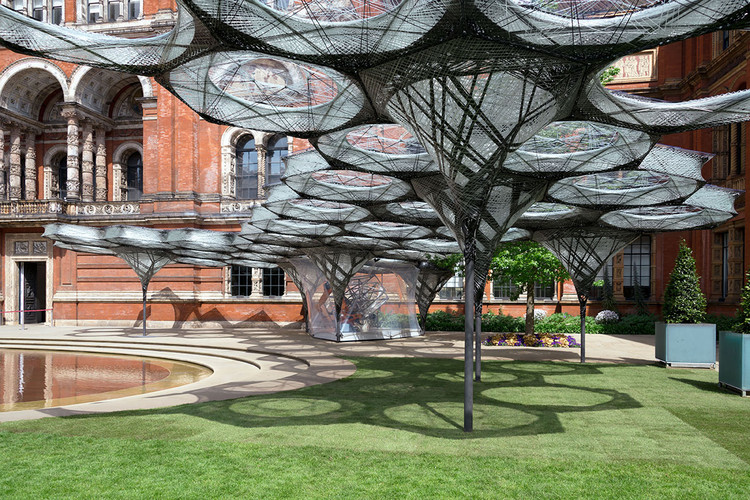
10. Elytra Filament Pavilion
The Elytra Filament Pavilion was designed by a team from the University of Stuttgart Computational and Structural Design Institute. The structure was built at the University of Stuttgart and assembled at Victoria and Alberts John Madejski Garden. The lightweight component of the pavilion was fabricated by robots. The nature-inspired lightweight form and fibrous structure of shells of flying beetles (Elytra). The 40 hexagonal components were assembled and constructed by robots for about four months. The primary materials utilized for construction are carbon and glass fibers.


































Leave a comment