Digital fabrication technologies such as 3D printing and CNC are no longer an “option for the advanced” students who work on architectural projects. Today, it is a necessity for any student who wants to survive in a highly competitive educational environment. Modern teachers expect instant solutions, and technologies develop so quickly that students who do not implement innovations in their architectural projects risk falling behind forever.
If you are a student who needs to work on architectural projects but doesn’t have time for this, don’t despair. You can use essay writing services from qualified experts. You will get help from an architect who knows how to deal with your project quickly.
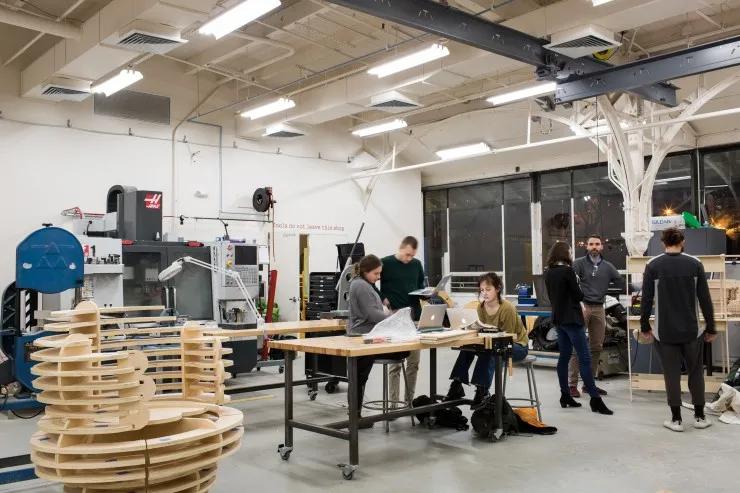

3D and CNC Milling Printing in Student Architectural Projects
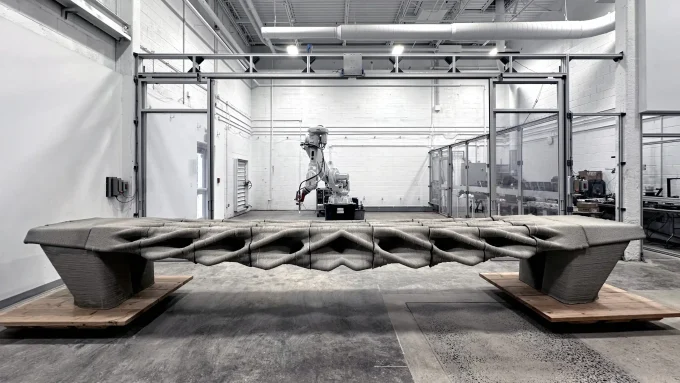
3D printing and CNC milling open up completely new possibilities for fast and affordable work on student architectural projects. You can use them to create both residential and non-residential buildings: from cozy one-story houses to impressive multi-story buildings, and the shapes of such buildings can be very diverse. Covered with a special concrete material, buildings printed on 3D printers are almost as good as traditional buildings in terms of their properties.
One of the most important areas of application of 3D printing and CNC milling in student architectural projects is the creation of affordable housing for people with low incomes. This technology allows you to develop unique projects while significantly reducing construction costs.
However, at the moment, there is no unified system of standards for the mass use of 3D printing and CNC milling in student architectural projects, which is why such projects are still implemented on an individual basis. Nevertheless, there are already many examples where students have successfully defended their projects with the use of 3D printing and CNC milling.
Advantages of Digital Fabrication Technologies
The benefits of digital fabrication technologies in student architectural projects are undeniable. One of the most compelling benefits is the ability to rapidly prototype and iterate designs. Students-architects can quickly create physical models of their concepts. This iterative process not only speeds up the design phase but also leads to more innovative and refined end results.
Another benefit is the democratization of design. Digital fabrication technologies make it easier for students to experiment with complex designs that would be too expensive or time-consuming using traditional methods.
The Curve Appeal by Chicago-based WATG (USA, Chicago) is an example of this democratization. The winning project in a competition organized by the American Institute of Architects and Branch Technology (USA, Chattanooga) shows how even small firms can use 3D printing to come up with innovative designs.
The building’s sleek, natural forms and futuristic designs, which are difficult to achieve using traditional construction methods, show how digital fabrication technologies can help a wide range of student-architects bring their creative ideas to life.
Challenges in Student Architectural Projects
Integrating digital fabrication technologies into architectural projects is not without its challenges. One of the main issues is the current limitations of the technologies themselves. Although 3D printing and CNC milling have advanced significantly, they are still evolving, with limitations in the size, speed, and range of materials that objects can be made of.
We can draw a parallel with the processes that professional architects create. For example, while large-scale projects like the 3D-printed office building in Dubai show the potential to create full-size buildings, the process remains slow and expensive compared to traditional construction methods, which may limit the application of such designs on a larger scale.
3D Printing and CNC Milling in Architectural Projects — Why Is It Profitable?
Production of architectural models is an important task for any student who studies architecture or design. The impression of teachers, professors, and supervisors depends on the quality of the model of the future project. Modeling using traditional methods is a long, labor-intensive, and very expensive process. 3D printing and CNC milling technologies allow you to significantly reduce the time it takes to make a model, improve the quality, bringing it as close as possible to the original. At the same time, the main part of the design work is carried out on a computer using modern 3D modeling software.
Advantages of 3D printing and CNC milling of architectural models:
● Speed of production: Just a few hours of 3D printer or CNC miller operation replaces 2- 3 months of manual labor
● Low cost of production: A special, affordable material based on gypsum may be used ● Finished models do not require painting; 3D printing completely reproduces any shades and colors in the CMYK palette
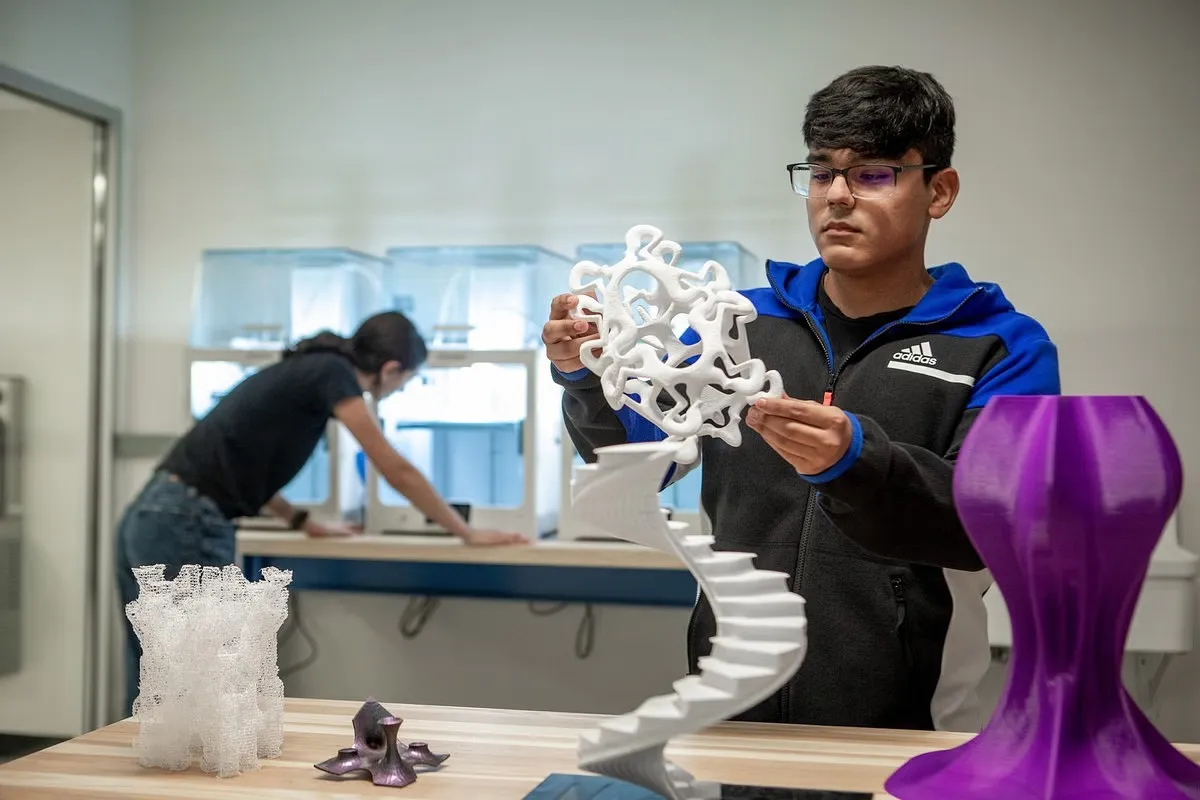
● High quality 3D printing: layer thickness from 90 microns, up to 390,000 colors, resolution 600×540 dpi; visual sample.
Technologies and Materials
For creating full-color architectural models, 3D printers of the ProJet x60 series from 3D Systems are often used. They are ideal for producing bright, high-precision demonstration models. The ProJet x60 series 3D printers create models using CJP technology from a special composite powder based on gypsum. The main advantages of such systems are high productivity, quality, and low cost of materials.
In addition, photopolymer 3D printers are often used when producing large and complex models. They are used to produce complex, highly detailed parts of projects with very small (less than a millimeter) elements. However, such 3D printers are not capable of printing colored objects, and the materials for them are significantly more expensive than gypsum.
Some students who study architecture and design also use 3D printers that print using ABS plastic. This is an opportunity to save on the production of a model, since the cost of plastic is lower than that of gypsum and photopolymers. However, it cannot be used to create full-color and highly detailed projects.
Significant Advancements
3D printing and CNC milling are not just new tools for a future architect; they are transformative forces that open up new horizons for innovation in architecture and design. As the technologies advance, they will play an increasingly important role in shaping the architecture of buildings.
It is necessary to conduct additional research in the following areas:
- Development of principles and recommendations for choosing the optimal type of 3D printer, CNC miller, and production technology depending on the characteristics and features of the project.
- Study of the design capabilities of structures built using digital fabrication technologies for the construction of buildings of various typologies.
- Development and testing of new building materials optimized for additive construction in order to ensure the desired performance characteristics and economic feasibility.
















Leave a comment